The Role of Global Physical Capacity Score in Key Parameters of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- PMID: 40507592
- PMCID: PMC12155748
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14113821
The Role of Global Physical Capacity Score in Key Parameters of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Abstract
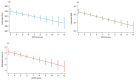
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. This study investigates the relationship between physical capacity, assessed by the Global Physical Capacity Score (GPCS), and MASLD-related parameters, including hepatic steatosis (CAP score), insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and body mass index (BMI). Methods: A cross-sectional analysis was performed on 204 individuals with MASLD (mean age: 50 years; 57.6% males). Participants underwent physical tests to determine their GPCS. Hepatic steatosis was assessed using FibroScan® (Echosens, Paris, France), and metabolic markers were collected from fasting blood samples. Statistical analyses included linear and logistic regression models adjusted for potential confounders. Results: A higher GPCS was inversely associated with CAP (β = -5.30; p < 0.05), HOMA-IR (β = -0.28; p < 0.001), and BMI (β = -0.96; p < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis confirmed a lower risk of severe hepatic steatosis (OR = 0.44; p < 0.05), obesity (OR = 0.39; p < 0.05), and insulin resistance (OR = 0.32; p < 0.001) in individuals with higher GPCS values. Conclusions: The GPCS may indicate MASLD severity and reflect metabolic and hepatic health. Our findings support the promotion of physical activity and suggest a potential role for GPCS in risk stratification and personalized interventions for patients with MASLD.
Keywords: Global Physical Capacity Score; HOMA-IR; body mass index; hepatic steatosis; metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Younossi Z.M., AlQahtani S.A., Funuyet-Salas J., Romero-Gómez M., Yilmaz Y., Keklikkiran C., Alswat K., Yu M.-L., Liu C.-J., Fan J.-G., et al. The Impact of Stigma on Quality of Life and Liver Disease Burden among Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JHEP Rep. 2024;6:101066. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

