Patient-Reported Outcomes with Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Low Back Pain from Vertebral Plana Deformities: A Case Series
- PMID: 40507726
- PMCID: PMC12155884
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14113964
Patient-Reported Outcomes with Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Low Back Pain from Vertebral Plana Deformities: A Case Series
Abstract
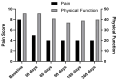
Objectives: This study evaluated peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) as a treatment for vertebra plana fractures, focusing on its impact on pain intensity, physical function, anxiety, depression, fatigue, social role participation, and pain interference. The goal was to assess whether PNS could serve as a minimally invasive alternative for managing pain in patients with severe vertebral fractures. Methods: Four patients with lumbar vertebra plana fractures received PNS implants for 60 days. Pain scores and PROMIS-29 domains (physical function, anxiety, depression, fatigue, social participation, and pain interference) were assessed at 30, 60, 90, 180, and 365 days post-implantation. Data analysis included mean and standard deviation calculations. Results: PNS led to marked improvements in pain-related outcomes. The average pain intensity scores dropped from 8.5 at baseline to 4.25 at one year, and pain interference scores declined from 61.75 to 54.75. Physical function initially decreased but improved from 38.5 at three months to 46.75 at one year. Changes in depression, anxiety, fatigue, and social participation were minimal, reflecting their multifactorial nature and limited response to pain relief alone. Conclusions: This case series suggests that PNS may significantly reduce pain and pain interference while enhancing physical function in patients with vertebra plana fractures. Its sustained benefits highlight PNS as a promising minimally invasive treatment, especially for those ineligible for traditional procedures. However, the limited improvement in psychological and social domains underscores the need for comprehensive care strategies. Further research is warranted to explore the broader role of PNS in managing vertebral fracture pain.
Keywords: acute pain; cancer pain; chronic pain; neuromodulation; peripheral nerve stimulation; plana fracture; temporary PNS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Nijs J., Kosek E., Chiarotto A., Cook C., Danneels L.A., Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C., Hodges P.W., Koes B., Louw A., Ostelo R., et al. Nociceptive, neuropathic, or nociplastic low back pain? The low back pain phenotyping (BACPAP) consortium’s international and multidisciplinary consensus recommendations. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024;6:e178–e188. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00324-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

