Protective Effect of a Hexapeptide Derived from Rotifer-Specific SCO-Spondin Against Beta-Amyloid Toxicity
- PMID: 40507923
- PMCID: PMC12154537
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115109
Protective Effect of a Hexapeptide Derived from Rotifer-Specific SCO-Spondin Against Beta-Amyloid Toxicity
Abstract
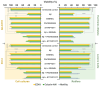
The Rotimer (rotifer-specific biopolymer) like SCO-spondin (R-SSPO/1), predicted as the main component of this biopolymer, is an adequate base for the design of functional small peptides. This macromolecule is interactive and protective against neurotoxic human-type beta-amyloid 1-42 aggregates (agg-Aβ). The current work presents biological investigations and predictable molecular interaction analysis of DSSNDL and PNCRDGSDE peptides that were synthesized based on the sequences of R-SSPO/1. Viability assays (NADH-dependent cellular reduction capacity, intracellular esterase activity, and motility) were performed on differentiated neuro-type cell cultures (SH-SY5Y and PC12) and on Rotimer-depleted rotifers (Euchlanis dilatata and Lecane bulla). A control peptide (STTRPTGTT), not found in Rotimer, was also included in the study. All three peptides are present in both rotifer and human proteomes. Among these small molecules, DSSNDL showed a significant protective effect against the toxicity of agg-Aβ both in vitro and in vivo and presumably interacted with its aggregates. The stagogram analysis of amyloid-peptide complexes and the possible bonding competition of these small molecules against aggregation-specific dyes on agg-Aβ surface suggest that DSSNDL affects the properties of these neurotoxic macromolecules. This effective hexapeptide can serve as a promising candidate for further investigations into the inactivation of beta-amyloid toxicity.
Keywords: SCO-spondin; beta-amyloid; biopolymer; rotifer.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Zita Galik-Olah was employed by the company iBioScience Ltd., Hungary. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021/János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- 2024/Translational Biomedicine Competence Centre of the Life Sciences Cluster of the Centre of Excellence for Interdisciplinary Research, Development and Innovation of the University of Szeged
- TKP2021-EGA-32/TKP2021-EGA-32 of the Ministry of Culture and Innovation of Hungary from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund, financed under the TKP2021-EGA funding scheme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

