Novel Tetraene Macrodiolides Are Effective Inducers of Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Jurkat Cells
- PMID: 40507950
- PMCID: PMC12155470
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115139
Novel Tetraene Macrodiolides Are Effective Inducers of Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Jurkat Cells
Abstract
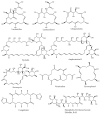
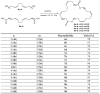
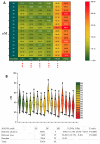
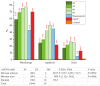
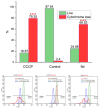
We synthesized 16 representatives of a new class of tetraene macrodiolides with two pharmacophore cis,cis-1,5-diene fragments of the molecule in their structure in rather high yields (from 67 to 84%), which, in turn, were synthesized by a catalytic intermolecular cyclocondensation reaction of α,ω-alka-nZ,(n+4)Z-diendiols with α,ω-alka-nZ,(n+4)Z-diendioic acids using Hf(OTf)4. The synthesis of starting substrates with 1Z,5Z-diene moieties with a high degree of stereoselectivity was carried out using the authors' original reaction of catalytic homo-cyclomagnesiation of O-containing allenes. The cytotoxic potential of the examined compounds was assessed using the following cell lines: Jurkat, K562, U937, HL60, HEK293, and Wi-38 (fibroblasts). Biological tests of the synthesized compounds showed a direct effect on mitochondrial biogenesis by the dissociation of oxidation and phosphorylation and the release of cytochrome P450 into the cell cytosol, as well as the induction of mitochondrial apoptosis. The selectivity index demonstrates significant variability, ranging from approximately 2.5 to 5.3 for Jurkat cells and from 3.0 to 5.8 for the other cell lines.
Keywords: 1,5-dienoic compounds; antitumor agents; apoptosis; cyclocondensation; homo-cyclomagnesiation; macrodiolides; tetraenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
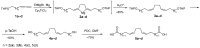
References
-
- Wang C., Xu L., Jia Z., Loh T.P. Recent applications of macrocycles in supramolecular catalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024;35:109075. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109075. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

