Ion Channel-Extracellular Matrix Interplay in Colorectal Cancer: A Network-Based Approach to Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling
- PMID: 40507957
- PMCID: PMC12154350
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115147
Ion Channel-Extracellular Matrix Interplay in Colorectal Cancer: A Network-Based Approach to Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling
Abstract
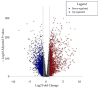
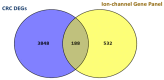
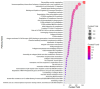
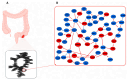
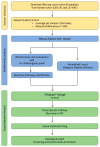
The progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) is driven by dynamic interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment, particularly the extracellular matrix (ECM). Ion channels, critical regulators of cellular signaling, have emerged as mediators of ECM remodeling and tumor aggressiveness. In this study, we integrate transcriptomic data from 185 CRC tumors and 157 adjacent normal tissues with network modeling to dissect the interplay between ion channels and the ECM. We identified 4036 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), including 188 ion channel-associated DEGs (IC-DEGs) enriched in ECM-related pathways, such as collagen assembly, matrix metalloproteinase regulation, and mechanotransduction. Structural equation modeling revealed an active CRC-ion channel module (CRC-IC) comprising 482 nodes and 422 edges, highlighting dysregulated interactions between ECM components (e.g., COL1A1, COL5A2, VCAN, LAMA4, LA-MA5, LAMC1), ion channels (e.g., TRPM5 and SLC16A1), and cytoskeletal regulators. Key nodes, including CHST11 and VCAN, were associated with ECM sulfation, tumor invasiveness, and immune evasion. Notably, survival was associated with MAPK1, SLC16A1, and ABCB4 in relation to patient prognosis. Our findings underscore the pivotal role of ion channels as co-factors in ECM dynamics in CRC, offering mechanistic insights into tumor-stroma crosstalk and identifying potential therapeutic targets to disrupt microenvironment-driven progression.
Keywords: causal network inference; colorectal cancer; extracellular matrix; ion channels; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

