Effect of Microglial Activity on Gut Microbiota in Rats with Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 40507989
- PMCID: PMC12154302
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115181
Effect of Microglial Activity on Gut Microbiota in Rats with Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between microglial activity and gut microbiota composition in a rat model of neuropathic pain (NP), and to evaluate how pregabalin treatment may influence these interrelated parameters. NP was simulated in rats via ligation and transection of the sciatic nerve. After confirming NP, the rats were randomly divided into treatment and control groups. Pregabalin (10 mg/kg) and the same dose of normal saline were administered to the treatment and control groups, respectively, on scheduled days. Microglial activity, cytokine levels, and the composition of the gut microbiota (assessed by the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio) were evaluated. Pregabalin treatment significantly reduced microglial activity (which was notably lower in the treatment group than in the control group) and modulated pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels. While the F/B ratio in the control group significantly increased after NP surgery, the treatment group showed an initial increase followed by a notable decrease, approaching pre-surgery levels by day 28. This finding suggests that pregabalin treatment in rats with NP ameliorates microglial activity and is associated with a beneficial shift in the gut microbiota composition.
Keywords: allodynia; brain–gut axis; microbiota; microglia; neuropathic pain; pregabalin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
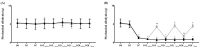
 ) Control group, (
) Control group, ( ) treatment group. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for intra-group comparisons and unpaired t-test for inter-group comparisons. Abbreviations: Control, control group; treatment, treatment group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 min after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. * p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.
) treatment group. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for intra-group comparisons and unpaired t-test for inter-group comparisons. Abbreviations: Control, control group; treatment, treatment group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 min after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. * p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.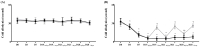
 ) Control group, (
) Control group, ( ) treatment group. Abbreviations: Control, control group; treatment, treatment group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 min after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for intra-group comparisons and unpaired t-test for inter-group comparisons.* p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.
) treatment group. Abbreviations: Control, control group; treatment, treatment group; D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery; before, before the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin; after, 60 min after the treatment of normal saline or pregabalin. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for intra-group comparisons and unpaired t-test for inter-group comparisons.* p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.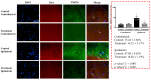

 ) Control group, (
) Control group, ( ) treatment group. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated ANOVA (followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for within-group comparisons over time and for between-group comparisons at specific time points). Abbreviations: D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery. * p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with D15 within the same group. ‡ p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.
) treatment group. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 6 per group). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated ANOVA (followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for within-group comparisons over time and for between-group comparisons at specific time points). Abbreviations: D0, before the surgery; D, day after the surgery. * p < 0.05 compared with D0 within the same group. † p < 0.05 compared with D15 within the same group. ‡ p < 0.05 compared with the control group at the same time point.References
-
- Finnerup N.B., Haroutounian S., Kamerman P., Baron R., Bennett D.L.H., Bouhassira D., Cruccu G., Freeman R., Hansson P., Nurmikko T., et al. Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain. 2016;157:1599–1606. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

