Molecular Imaging: Unveiling Metabolic Abnormalities in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 40508051
- PMCID: PMC12154437
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115242
Molecular Imaging: Unveiling Metabolic Abnormalities in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
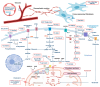
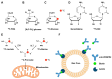
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most aggressive malignancies globally, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 13%. This poor prognosis stems from late-stage diagnosis and intrinsic resistance to conventional therapies, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy. A hallmark of PC is oncogene-driven metabolic reprogramming-notably mediated by mutations in KRAS and other key pathways-which fuels tumor progression and undermines the efficacy of neoadjuvant treatments. Consequently, there is a pressing demand for non-invasive techniques capable of mapping metabolic alterations at both the tumor microenvironmental and systemic levels. This review will discuss molecular imaging techniques that identify metabolic changes within the tumor microenvironment. By bridging preclinical insights with clinical applications, we highlight how these innovations promise to revolutionize PC diagnosis, treatment stratification, and therapeutic monitoring, ultimately paving the way for precision oncology.
Keywords: metabolic imaging; molecular imaging; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolism of pancreatic cancer: paving the way to better anticancer strategies.Mol Cancer. 2020 Mar 2;19(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01169-7. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32122374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming of drug resistance in pancreatic cancer: mechanisms and effects.Mol Aspects Med. 2025 Jun;103:101368. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2025.101368. Epub 2025 May 20. Mol Aspects Med. 2025. PMID: 40398192 Review.
-
Glucose metabolism and tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer: A key link in cancer progression.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 12;13:1038650. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1038650. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36578477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting hypoxic tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 13;14(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01030-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33436044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic KRAS-Driven Metabolic Reprogramming in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Utilizes Cytokines from the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr;10(4):608-625. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0297. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32046984 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

