Molecular Insights into Neurological Regression with a Focus on Rett Syndrome-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40508170
- PMCID: PMC12154281
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115361
Molecular Insights into Neurological Regression with a Focus on Rett Syndrome-A Narrative Review
Abstract
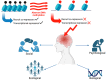
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a multisystem neurological disorder. Pathogenic changes in the MECP2 gene that codes for methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) in RTT lead to a loss of previously established motor and cognitive skills. Unravelling the mechanisms of neurological regression in RTT is complex, due to multiple components of the neural epigenome being affected. Most evidence has primarily focused on deciphering the complexity of transcriptional machinery at the molecular level. Little attention has been paid to how epigenetic changes across the neural epigenome in RTT lead to neurological regression. In this narrative review, we examine how pathogenic changes in MECP2 can disrupt the balance of the RTT neural epigenome and lead to neurological regression. Environmental and genetic factors can disturb the balance of the neural epigenome in RTT, modifying the onset of neurological regression. Methylation changes across the RTT neural epigenome and the consequent genotoxic stress cause neurons to regress into a senescent state. These changes influence the brain as it matures and lead to the emergence of specific symptoms at different developmental periods. Future work could focus on epidrugs or epi-editing approaches that may theoretically help to restore the epigenetic imbalance and thereby minimise the impact of genotoxic stress on the RTT neural epigenome.
Keywords: Rett syndrome; epigenome; methylation; neurological regression.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. was a past Trial Research Methodologist on the Sarizotan Clinical Trial (Sarizotan/001/II/2015) and a Research Manager on the Anavex clinical trial for RTT (Anavex Life Sciences Corp. [Protocol Number: ANAVEX2-73-RS-002/003]). J.S. is also an advisor for Reverse Rett. P.S. was on the advisory board for Acadia Pharmaceuticals. P.S. was a past Principal Investigator (PI) on the Newron Pharmaceuticals SpA (Sarizotan/001/II/2015) and Anavex Life Sciences Corp. trials (ANAVEX2-73-RS-002 and ANAVEX2-73-RS-003) in RTT. P.S. is the co-inventor of the HealthTrackerTM and is the Chief Executive Officer and shareholder in HealthTrackerTM.
Figures



References
-
- Lewis J.D., Meehan R.R., Henzel W.J., Maurer-Fogy I., Jeppesen P., Klein F., Bird A. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992;69:905–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

