Divergent Functions of Rap1A and Rap1B in Endothelial Biology and Disease
- PMID: 40508181
- PMCID: PMC12155061
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26115372
Divergent Functions of Rap1A and Rap1B in Endothelial Biology and Disease
Abstract
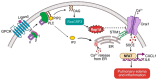
Rap1A and Rap1B are closely related small GTPases that regulate endothelial adhesion, vascular integrity, and signaling pathways via effector domain interactions, with downstream effectors controlling integrins and cadherins. Although both isoforms are essential for vascular development, recent studies using endothelial-specific knockout models have uncovered distinct, non-redundant functions. Rap1B is a key regulator of VEGFR2 signaling, promoting angiogenesis, nitric oxide production, and immune evasion in tumors while restraining proinflammatory signaling in atherosclerosis. In contrast, Rap1A unexpectedly functions as a modulator of endothelial calcium homeostasis by restricting Orai1-mediated store-operated calcium entry, thereby limiting inflammatory responses and vascular permeability. New insights into Rap1 regulation highlight the roles of context-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors, such as RasGRP3, and non-degradative ubiquitination in effector selection. Emerging data suggest that isoform-specific interactions between the Rap1 hypervariable regions and plasma membrane lipids govern their localization to distinct nanodomains, potentially influencing downstream signaling specificity. Together, these findings redefine the roles of Rap1A and Rap1B in endothelial biology and highlight their relevance in diseases such as tumor angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, and inflammatory lung injury. We discuss the therapeutic implications of targeting Rap1 isoforms in vascular pathologies and cancer, emphasizing the need for isoform-specific strategies that preserve endothelial homeostasis.
Keywords: Rap GEF (Rap1 Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor); Rap1A; Rap1B; RasGRP3; VEGFR2; angiogenesis; calcium signaling; inflammation; nitric oxide; vascular immunosuppression; vascular permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rap1A Modulates Store-Operated Calcium Entry in the Lung Endothelium: A Novel Mechanism Controlling NFAT-Mediated Vascular Inflammation and Permeability.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Nov;44(11):2271-2287. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321458. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 39324266 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1a is a key regulator of fibroblast growth factor 2-induced angiogenesis and together with Rap1b controls human endothelial cell functions.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5803-10. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00393-08. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625726 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Rap1 (Ras-Association Proximate 1) Restricts Inflammatory Signaling to Protect From the Progression of Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Feb;41(2):638-650. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315401. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33267664 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Targeting Endothelial Rap1B to Overcome Vascular Immunosuppression in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9853. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189853. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAP GTPases and platelet integrin signaling.Platelets. 2019;30(1):41-47. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2018.1476681. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Platelets. 2019. PMID: 29863951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

