Comprehensive Simulation-Based Evaluation of Gamma Radiation Shielding Performance of Bismuth Oxide- and Tungsten Oxide-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Nuclear Medicine Occupational Safety
- PMID: 40508734
- PMCID: PMC12158205
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17111491
Comprehensive Simulation-Based Evaluation of Gamma Radiation Shielding Performance of Bismuth Oxide- and Tungsten Oxide-Reinforced Polymer Composites for Nuclear Medicine Occupational Safety
Abstract
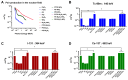
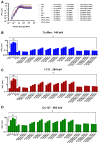
This study employs simulation tools to design and evaluate lightweight, lead-free polymer composites incorporating polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethylene (PE), and polyetherimide (PEI) for gamma radiation shielding in nuclear medicine. Targeting clinically relevant photon energies from Tc-99m (140 keV), I-131 (364 keV), and Cs-137 (662 keV), composites' structural and shielding performance with Bi2O3 and WO3 was assessed using XCOM and Phy-X/PSD. PEI emerged as the most suitable polymer for load-bearing and thermally exposed applications, offering superior mechanical stability and dimensional integrity. Bi2O3-WO3 fillers for Tc-99m achieved a ~7000-fold increase in MAC, I-131 ~2063-fold, and Cs-137 ~1370-fold compared to PbO2. The PEI-75Bi2O3-25WO3 achieved a ~21-fold reduction in half-value layer (HVL) compared to lead for Tc-99m. For higher-energy isotopes of I-131 and Cs-137, HVL reductions of ~0.44-fold and ~0.08-fold, respectively, were achieved. The results demonstrate that high-Z dual filler polymer composites have an equal or enhanced attenuation properties to lead-based shielding, whilst also enhancing the polymer composites' mechanical and thermal characteristics. As the use of ionizing radiation increases, so does the potential risks; high-Z dual filler polymer composites provide a sustainable, lightweight, non-toxic alternative to conventional lead shielding.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; Phy-X/PSD; XCOM simulation; bismuth oxide; gamma shielding; polymer composites; radiation attenuation; radiation protection; shielding materials; tungsten oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Glasser O. Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen and the Early History of the Roentgen Rays. Norman Publishing; San Francisco, CA, USA: 1993.
-
- Mentana A., Quaresima V., Kundrát P., Guardamagna I., Lonati L., Iaria O., Previtali A., Amantini G.S., Lunati L., Boretti V. Mapping Neutron Biological Effectiveness for DNA Damage Induction as a Function of Incident Energy and Depth in a Human Sized Phantom. Sci. Rep. 2025;15:2209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85879-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

