Preparation of Highly Antibacterial MXene Nanofiltration Membranes and Investigation of Their Separation Performance
- PMID: 40508736
- PMCID: PMC12157103
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17111493
Preparation of Highly Antibacterial MXene Nanofiltration Membranes and Investigation of Their Separation Performance
Abstract
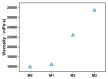
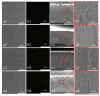
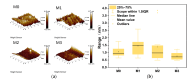
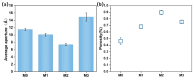
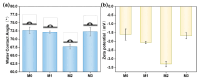
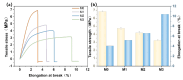
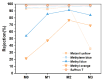
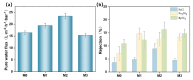
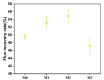
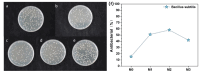
In this study, polyethersulfone (PES)/sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) composite nanofiltration membranes doped with different contents of monolayer titanium carbide nanosheets (Ti3C2TX) were prepared by the nonsolvent induced phase inversion (NIPS) method. The effects of Ti3C2TX on membrane structure, separation performance and antibacterial activity were investigated systematically. The results demonstrated that the viscosity of the casting solution increased significantly with the increasing content of Ti3C2TX. In addition, the pore size of the membrane surface first decreased and then increased; porosity and hydrophilicity were optimized synchronously; and the density of negative charges on the surface increased. The M2 membrane showed a rejection rate of more than 90% for Metanil yellow (MY) and methylene blue (MEB). The order of salt ion rejection rates was magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) > sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) > sodium chloride (NaCl), and water flux reached the peak (18.5 L/m2·h·bar). The antibacterial activity of the M2 membrane was significantly enhanced, and its antibacterial rate against Bacillus subtilis increased from 15% (M0) to 58%. This phenomenon was attributed to the synergistic mechanism of the Ti3C2TX physical capture effect, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and sharp edge damage to bacterial cell membranes. This study provides theoretical support and a technical path for the development of MXene composite membranes with high separation efficiency and excellent antibacterial properties.
Keywords: PES/SPES membrane; Ti3C2TX; antibacterial activity; blend membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preparation of Highly Antibacterial Polyethersulfone/Sulfonated Polyethersulfone Blend Composite Membrane and Research on Its Dye Separation Performance.Molecules. 2025 Feb 8;30(4):781. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040781. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005093 Free PMC article.
-
Novel antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone membrane prepared by embedding nitrogen-doped carbon dots for efficient salt and dye rejection.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jun;111:110787. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110787. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32279812
-
Removal of Scale-Forming Ions and Oil Traces from Oil Field Produced Water Using Graphene Oxide/Polyethersulfone and TiO2 Nanoribbons/Polyethersulfone Nanofiltration Membranes.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 24;14(13):2572. doi: 10.3390/polym14132572. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808619 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-polyphenol cross-linked titanium carbide membranes with stable interlayer spacing for efficient wastewater treatment.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Dec 15;628(Pt B):649-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.092. Epub 2022 Aug 18. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 36027775
-
Influence of monomers involved in the fabrication of a novel PES based nanofiltration thin-film composite membrane and its performance in the treatment of common effluent (CETP) textile industrial wastewater.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021 Mar 16;19(1):515-529. doi: 10.1007/s40201-021-00624-x. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34150255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng L.F., Yan H.Y., Liang C., Kato N., Jeon S., Takagi R., Matsuyama H. Effect of Molecular Weight of Sulfonated Poly (ether sulfone) (SPES) on the Mechanical Strength and Antifouling Properties of Poly (ether sulfone)/SPES Blend Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017;56:11302–11311. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b02996. - DOI
-
- Huang X., Zhang Z., Kong X., Sun Y., Zhu C., Liu P., Pang J., Jiang L., Wen L. Engineered PES/SPES nanochannel membrane for salinity gradient power generation. Nano Energy. 2019;59:354–362. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.02.056. - DOI
-
- Akin E., Gharibzahedi T.M.S., Qiu H., Aliyeva A., Altintas Z. Chitosan-functionalized PVDF and PES membranes integrated by epitope-imprinted polymers for targeted hepatitis A virus capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2024;709:123084. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2024.123084. - DOI
-
- Athira V.B., Mohanty S., Nayak S. Preparation and characterization of porous polyethersulfone (PES) membranes with improved biocompatibility by blending sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) and cellulose acetate (CA)–A comparative study. Mater. Today Commun. 2020;25:101544.
-
- Almanassra I.W., Lubna J., Anjaneyulu C., Abushawish A., Shanableh A., Ali Atieh M. Unveiling the relationship between MOF porosity, particle size, and polyethersulfone membranes properties for efficient decontamination of dye and organic matter. Chem. Eng. J. 2023;471:144616. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.144616. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

