Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Effect of Phloroglucinol-Enriched Whey Protein Isolate Fibrillar Coating on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- PMID: 40508757
- PMCID: PMC12157878
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17111514
Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenic Effect of Phloroglucinol-Enriched Whey Protein Isolate Fibrillar Coating on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Abstract
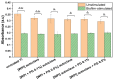
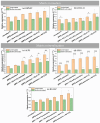
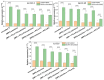
Biomaterials play a crucial role in the long-term success of bone implant treatment. The accumulation of bacterial biofilm on the implants induces inflammation, leading to implant failure. Modification of the implant surface with bioactive molecules is one of the strategies to improve biomaterial compatibility and limit inflammation. In this study, whey protein isolate (WPI) fibrillar coatings were used as a matrix to incorporate biologically active phenolic compound phloroglucinol (PG) at different concentrations (0.1% and 0.5%) on titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) scaffolds. Successful Ti6Al4V coatings were validated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), showing a decrease in %Ti and increases in %C, %N, and %O, which demonstrate the presence of the protein layer. The biological activity of PG-enriched WPI (WPI/PG) coatings was assessed using bone-forming cells, human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs). WPI/PG coatings modulated the behavior of BM-MSCs but did not have a negative impact on cell viability. A WPI with higher concentrations of PG increased gene expression relative to osteogenesis and reduced the pro-inflammatory response of BM-MSCs after biofilm stimulation. Autoclaving reduced WPI/PG bioactivity compared to filtration. By using WPI/PG coatings, this study addresses the challenge of improving osteogenic potential while limiting biofilm-induced inflammation at the Ti6Al4V surface. These coatings represent a promising strategy to enhance implant bioactivity.
Keywords: Ti6Al4V; biofilm; fibrillar coating; inflammation; osseointegration; osteogenesis; phenolic coating; stem cells; whey protein isolate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Seo B.Y., Son K., Son Y.-T., Dahal R.H., Kim S., Kim J., Hwang J., Kwon S.-M., Lee J.-M., Lee K.-B., et al. Influence of Dental Titanium Implants with Different Surface Treatments Using Femtosecond and Nanosecond Lasers on Biofilm Formation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023;14:297. doi: 10.3390/jfb14060297. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

