Sawdust as a Byproduct of Wood Processing: Properties, Applications and a Reinforcing Filler in Hybrid Polymer Composites
- PMID: 40508767
- PMCID: PMC12157330
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17111523
Sawdust as a Byproduct of Wood Processing: Properties, Applications and a Reinforcing Filler in Hybrid Polymer Composites
Abstract
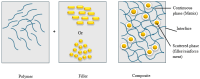
There is a sizeable amount of sawdust produced from wood industries such as timber and furniture. In the past, sawdust has been utilized as a fuel source and in the manufacturing of furniture. Based on the limited use of sawdust, there is plenty of sawdust accessible from the industries. Sawdust is the material of choice due to its cost effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and biodegradability. However, if sawdust is not appropriately disposed or utilized better, it may have negative impact on the aquatic life and organic products. Hence, this review paper discusses the best possible methods or proper routes for the utilization of sawdust to benefit the environment, society, and the economy at large. Sawdust possesses superior capabilities as a reinforcing filler in various polymer matrices for advanced applications. This paper provides an in-depth discussion on sawdust hybrid composites in comparison to other natural fibres hybrid composites. The applications of various sawdust hybrid polymer composites for specific systems are also mentioned. Furthermore, the morphology and preparation of the sawdust/polymer composites and/or sawdust hybrid polymers composites are also discussed since it is well known that the properties of the natural fibre composites are affected by the preparation method and the resultant morphology. Based on the above, the current paper also plays a critical role in providing more information about waste to value added products.
Keywords: hybrid systems; natural fibre; polymer composites; sawdust; wood-waste.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polymer Composites Reinforced with Residues from Amazonian Agro-Extractivism and Timber Industries: A Sustainable Approach to Enhancing Material Properties and Promoting Bioeconomy.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;16(23):3282. doi: 10.3390/polym16233282. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Polyurethane Composites with Coffee Grounds and Wood Sawdust.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;16(1):278. doi: 10.3390/ma16010278. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36614616 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Characterisation of Wood Polymer Composites Using Sustainable Raw Materials.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 4;14(15):3183. doi: 10.3390/polym14153183. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956698 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal, Mechanical, Morphological and Aesthetical Properties of Rotational Molding PE/Pine Wood Sawdust Composites.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jan 4;14(1):193. doi: 10.3390/polym14010193. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35012216 Free PMC article.
-
On the Use of Dolomite as a Mineral Filler and Co-Filler in the Field of Polymer Composites: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 13;14(14):2843. doi: 10.3390/polym14142843. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zafeer M.-K., Prabhu R., Rao S., Mahesha G.T., Bhat K.S. Mechanical characteristics of sugarcane bagasse fibre reinforced polymer composites: A review. Cogent Eng. 2023;10:220090310. doi: 10.1080/23311916.2023.2200903. - DOI
-
- Deepan S., Jeyakumar R., Mohankumar V., Manojkumar A. Influence of rice husk fillers on mechanical properties of banana/epoxy natural fiber hybrid composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2022;74:575–580. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.09.459. - DOI
-
- Arjmandi R., Hassan A., Majeed K., Zakaria Z. Rice husk filled polymer composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015;2015:501471. doi: 10.1155/2015/501471. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

