Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA
- PMID: 40509043
- PMCID: PMC12153630
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15111577
Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA
Abstract
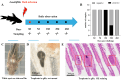
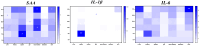
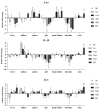
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and serum amyloid A (SAA) are key pro-inflammatory mediators in the regulation of immune responses. The hypothesis posits that their expression varies with the progression of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Ich) infection and may serve as predictors of disease outcome. To elucidate their spatiotemporal dynamics, the full-length CDS of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA in Pelteobagrus vachelli were cloned, and then their mRNA levels were tracked from infection onset (day 0) to resolution (day 40) or mortality in seven tissues. Key findings revealed a surge in IL-1β expression in the kidney and SAA expression in the spleen at 5 days post-infection (dpi), coinciding with no visible symptoms. Significant SAA elevation in the head kidney was observed at 10 dpi, preceding the emergence of white spots on the skin. This was followed by gill-specific SAA downregulation at 20 dpi, when 40% of fish presented with white spots. Complete clinical resolution by 40 dpi correlated with reduced hepatic SAA and branchial IL-1β levels. Notably, the concurrent upregulation of all three mediators occurred exclusively in the skin of moribund individuals. These findings identify potential biomarkers for tracking host inflammatory responses in ichthyophthiriasis.
Keywords: Ichthyophthirius multifiliis; Pelteobagrus vachelli; interleukin-1β; interleukin-6; serum amyloid A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
cMOS enhanced the mucosal immune function of skin and gill of goldfish (Carassius auratus Linnaeus) to improve the resistance to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022 Jul;126:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.05.024. Epub 2022 May 18. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35595060
-
Serum amyloid A induces interleukin-1β secretion from keratinocytes via the NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 inflammasome.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Feb;179(2):344-53. doi: 10.1111/cei.12458. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25231464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chlorella vulgaris extract conjugated magnetic iron nanoparticles in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Growth promoting, immunostimulant and antioxidant role and combating against the synergistic infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Aeromonashydrophila.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Feb;145:109352. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109352. Epub 2024 Jan 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38171430
-
Immune responses of fish to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Ich): A model for understanding immunity against protozoan parasites.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Apr;93:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30630003 Review.
-
Ichthyophthiriasis: emphases on the epizootiology.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2013 Aug;57(2):91-101. doi: 10.1111/lam.12079. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23565747 Review.
References
-
- Coyne R.S., Hannick L., Shanmugam D., Hostetler J.B., Brami D., Joardar V.S., Johnson J., Radune D., Singh I., Badger J.H., et al. Comparative genomics of the pathogenic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, its free-living relatives and a host species provide insights into adoption of a parasitic lifestyle and prospects for disease control. Genome Biol. 2011;12:R100. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-r100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

