Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria
- PMID: 40509503
- PMCID: PMC12154344
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14111975
Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria
Abstract
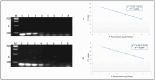
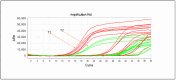
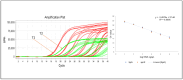
Microbial detection in milk is crucial for food safety and quality, as beneficial and harmful microorganisms can affect consumer health and dairy product integrity. Identifying and quantifying these microorganisms helps prevent contamination and spoilage. The study employs advanced molecular techniques to detect and quantify the genomic DNA for the target hydrolytic enzyme coding genes lipA and aprX based on the multi-align sequence conserved region, specific primer pair, and hydrolysis probes designed using the singleplex qPCR and multiplex qPCR. Cultured isolates and artificially contaminated sterilized ultra-high-temperature (UHT) milk were analyzed for their specificity, cross-reactivity, and sensitivity. The finding indicated that strains with lipA and aprX genes were amplified while the other strains were not amplified. This indicated that the designed primer pairs/probes were very specific to the target gene of interest. The specificity of each design primer pair was checked using SYBR Green qPCR using 16 different isolate strains from the milk sample. The quantification specificity of each strain target gene was deemed to be with a mean Ct value for positive pseudomonas strain > 16.98 ± 1.76 (p < 0.0001), non-pseudomonas positive strain ≥ 27.47 ± 1.25 (p < 0.0001), no Ct for the negative control and molecular grade water. The sensitivity limit of detection (LOD) analyzed based on culture broth and milk sample was >105 and >104 in PCR amplification while it was >104 and >103 in real-time qPCR, respectively. At the same time, the correlation regression coefficient of the standard curve based on the pure culture cell DNA as the DNA concentration serially diluted (20 ng/µL to 0.0002 ng/µL) was obtained in multiplex without interference and cross-reactivity, yielding R2 ≥ 0.9908 slope (-3.2591) and intercepting with a value of 37, where the efficiency reached the level of 95-102% sensitivity reached up to 0.0002 ng/µL concentration of DNA, and sensitivity of microbial load was up to 1.2 × 102 CFU/mL. Therefore, multiplex TaqMan qPCR simultaneous amplification was considered the best method developed for the detection of the lipA and aprX genes in a single tube. This will result in developing future simultaneous (three- to four-gene) detection of spoilage psychrotrophic bacteria in raw milk.
Keywords: hydrolytic enzymes; microbial detection; multiplex qPCR; psychrotrophic bacteria; raw milk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous quantification of the most common and proteolytic Pseudomonas species in raw milk by multiplex qPCR.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Feb;105(4):1693-1708. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11109-0. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33527148 Free PMC article.
-
The Extracellular Protease AprX from Pseudomonas and its Spoilage Potential for UHT Milk: A Review.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2019 Jul;18(4):834-852. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12452. Epub 2019 May 10. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2019. PMID: 33336988
-
Rapid Identification of Pseudomonas fluorescens Harboring Thermostable Alkaline Protease by Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.J Food Prot. 2022 Mar 1;85(3):414-423. doi: 10.4315/JFP-21-272. J Food Prot. 2022. PMID: 34855939
-
The Biodiversity of the Microbiota Producing Heat-Resistant Enzymes Responsible for Spoilage in Processed Bovine Milk and Dairy Products.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 1;8:302. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00302. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28298906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Development in Detection and Control of Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Dairy Production: Ensuring Milk Quality.Foods. 2024 Sep 13;13(18):2908. doi: 10.3390/foods13182908. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39335837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martínez N., Martín M.C., Herrero A., Fernández M., Alvarez M.A., Ladero V. QPCR as a Powerful Tool for Microbial Food Spoilage Quantification: Significance for Food Quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011;22:367–376. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.04.004. - DOI
-
- Dash K.K., Fayaz U., Dar A.H., Shams R., Manzoor S., Sundarsingh A., Deka P., Khan S.A. A Comprehensive Review on Heat Treatments and Related Impact on the Quality and Microbial Safety of Milk and Milk-Based Products. Food Chem. Adv. 2022;1:100041. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100041. - DOI
-
- Ziyaina M., Rasco B., Sablani S.S. Rapid Methods of Microbial Detection in Dairy Products. Food Control. 2020;110:107008. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.107008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

