FGFR1 overexpression promotes resistance to PI3K inhibitor alpelisib in luminal breast cancer cells through receptor tyrosine kinase signaling-mediated activation of the estrogen receptor
- PMID: 40510030
- PMCID: PMC12159599
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2024.181
FGFR1 overexpression promotes resistance to PI3K inhibitor alpelisib in luminal breast cancer cells through receptor tyrosine kinase signaling-mediated activation of the estrogen receptor
Abstract
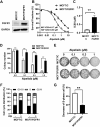
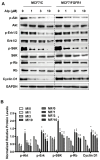
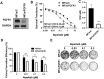
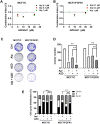
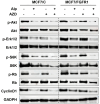
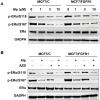
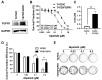
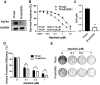
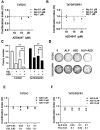
Aim: Resistance to PI3K inhibitor alpelisib is an emerging challenge in breast cancer treatment. FGFR1 is frequently amplified in breast cancer. We investigated FGFR1 overexpression-mediated alpelisib resistance and its mechanism. Methods: CCK-8, colony formation, and cell cycle assays assessed FGFR1 overexpression-induced alpelisib resistance in MCF-7 and T47D cells. FGFR1 siRNA knockdown validated FGFR1's role. Akt, Erk, and ER signaling were analyzed by Western blot. Synergistic effects of alpelisib with AZD4547 and fulvestrant were evaluated using the combination index. Results: FGFR1 overexpression conferred alpelisib resistance in MCF-7 and T47D cells, evidenced by increased viability, colony formation, and S-phase accumulation post alpelisib treatment. Knockdown of FGFR1 reverse alpelisib resistance in FGFR1 overexpressing MCF-7 and T47D cells. Resistance correlated with sustained activation of Akt and Erk1/2 pathways (p-Akt, p-Erk1/2, p-S6K, p-Rb) and attenuated suppression of ERα phosphorylation (S118/S167), highlighting RTK-ER crosstalk. Combining alpelisib with AZD4547 synergistically inhibited growth and suppressed both RTK signaling and ERα phosphorylation. While alpelisib-fulvestrant was effective, adding AZD4547 further enhanced inhibition, supporting triple therapy to overcome resistance. Conclusion: Our findings establish FGFR1 as a key mediator of alpelisib resistance in ER+ breast cancer. Combining FGFR1 inhibitors with alpelisib-based therapies offers a viable approach for FGFR1-overexpressing tumors.
Keywords: AZD4547; FGFR1; PI3K; alpelisib; estrogen receptor; fulvestrant; resistance.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Yang X is an editor on the Editorial Board of the journal Cancer Drug Resistance. Yang X is not involved in any steps of editorial processing, notably including reviewer selection, manuscript handling, or decision making. Godefridus J. Peters and all co-authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest. The other authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FGFR1 Overexpression Induces Cancer Cell Stemness and Enhanced Akt/Erk-ER Signaling to Promote Palbociclib Resistance in Luminal A Breast Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Nov 4;10(11):3008. doi: 10.3390/cells10113008. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831231 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine IGF-I/insulin receptor axis compensates for inhibition of AKT in ER-positive breast cancer cells with resistance to estrogen deprivation.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R55. doi: 10.1186/bcr3449. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23844554 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR1 Amplification Mediates Endocrine Resistance but Retains TORC Sensitivity in Metastatic Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR+) Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 1;25(21):6443-6451. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0138. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31371343 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus versus alpelisib in advanced hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative breast cancer: targeting different nodes of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway with different clinical implications.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 6;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01271-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32252811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: mechanisms and role in endocrine resistance.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 8;14:1406951. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406951. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39040443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
