Otogenic Lateral and Transverse Sinovenous Thrombosis in a Child: A Case Report
- PMID: 40510074
- PMCID: PMC12162127
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84045
Otogenic Lateral and Transverse Sinovenous Thrombosis in a Child: A Case Report
Abstract
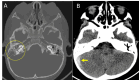
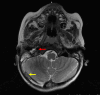
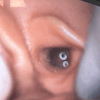
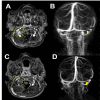
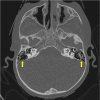
Acute otitis media (AOM) is common in children, but intracranial complications such as meningitis, cerebral abscess, and cerebral venous sinus thrombosis are rare and can be potentially life-threatening. This case describes a three-year-old boy who presented to the emergency room following one week of coryza, fever, cough, malaise, and otalgia, along with three days of severe headache and vomiting. Physical examination revealed hyperemia and bulging of both tympanic membranes on otoscopy, along with an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and elevated levels of leukocytes, C-reactive protein, and D-dimer. Cranial computed tomography scan revealed soft tissue density occupying the mastoid cells bilaterally and enlargement of the right transverse and sigmoid venous sinuses; magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed thrombophlebitis in the right internal jugular vein and thrombosis in the transverse and sigmoid sinuses. The diagnosis was bilateral AOM with otogenic lateral right sinus thrombosis, and the patient had also developed bilateral sixth cranial nerve paresis and cerebellitis. He made a full recovery without any sequelae, following treatment that included the placement of tympanostomy tubes in both ears, a 21-day course of systemic antibiotics, and two weeks of anticoagulation therapy with low molecular-weight heparin. Follow-up showed clinical improvement and normalization of inflammatory markers; the radiological images showed complete resolution of thrombosis. Since otogenic lateral sinus thrombosis symptoms can mimic uncomplicated AOM, maintaining a high index of suspicion is essential in preventing fatal outcomes and ensuring favorable recovery in pediatric patients.
Keywords: acute media otomastoiditis; anticoagulants; child; intracranial thrombosis; sinus thrombosis.
Copyright © 2025, Rosero-Castillo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Otogenic lateral sinovenous thrombosis in children: a case series from a single centre and narrative review. Trapani S, Stivala M, Lasagni D, Rosati A, Indolfi G. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32912560/ J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29:105184. - PubMed
-
- Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. deVeber G, Andrew M, Adams C, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11496852/ N Engl J Med. 2001;345:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Updated guidelines for the management of acute otitis media in children by the Italian Society of Pediatrics: treatment. Marchisio P, Galli L, Bortone B, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31876601/ Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019;38:0–21. - PubMed
-
- Management of paediatric otogenic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a systematic review. Wong BY, Hickman S, Richards M, Jassar P, Wilson T. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26769686/ Clin Otolaryngol. 2015;40:704–714. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
