Global analysis of excitotoxicity-induced alterations in RNA structure and RNA-protein binding in neurons
- PMID: 40510133
- PMCID: PMC12159502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112595
Global analysis of excitotoxicity-induced alterations in RNA structure and RNA-protein binding in neurons
Abstract
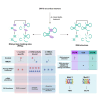
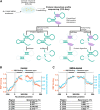
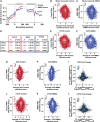
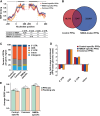
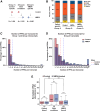
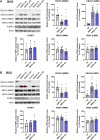
Excitotoxicity and altered RNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are two prevalent hallmarks in multiple neurodegenerative disorders. However, global effects of excitotoxicity on RNA secondary structure and RNA-protein interactions are largely unknown. To address this, we have performed protein interaction profile sequencing (PIP-seq) in NMDA-treated primary neurons. Our results show that NMDA treatment alters RNA structure, which correlates, in opposite directions depending on the intragenic region, with changes in mRNA abundance. Moreover, NMDA treatment increases and alters RNA-protein binding sites defining subsets of transcripts functionally associated with synaptic functions and neurodegenerative disorders. Finally, we identify two RNA motifs enriched in protein binding after NMDA treatment, and several RBPs binding to them in vitro, including CELF6 and YBX3, which show NMDA-dependent changes in their protein levels. Overall, we provide extensive datasets that can be leveraged to bridge the mechanistic gap between two hallmarks of neurodegeneration: excitotoxicity and RNA regulation by RBPs.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Neuroscience.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

