Molecular targets and mechanisms of cortex mori for lung cancer treatment: a network pharmacology study, molecular docking and in vitro and in vivo experimental validation
- PMID: 40510163
- PMCID: PMC12158998
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1587856
Molecular targets and mechanisms of cortex mori for lung cancer treatment: a network pharmacology study, molecular docking and in vitro and in vivo experimental validation
Abstract
Introduction: The cortex mori comes from the white endothelium of the young root of Morus alba L., and its medical value was first described in Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Classic on Materia Medical of Shennong). It was originally intended to purge lung, relieve asthma and reduce swelling. More and more studies reported that its pharmacological effects include analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, antiasthmatic, hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic and anti-diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Accumulating clinical evidences exhibited that it can treat asthma, pneumonia and lung cancer. However, a comprehensive mechanism of cortex mori in the treatment of lung cancer needs to be further elucidated.To investigate the effect of cortex mori and its active components against lung cancer and explore its action and mechanism through network pharmacological analysis combined with biological experiments in vitro and In vivo.
Methods: GeneCards database was searched for the disease targets of lung cancer, and a Chinese medicine database, Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP), was used to screen cortex mori for its active components and targets. Targets related to lung cancer and action targets related to cortex mori were crossed. Protein-protein interactions (PPI) and gene ontologies (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) were analyzed for intersection genes. In order to determine whether cortex mori affects lung cancer, MTS, wound healing, Western-blot, Hoechst assay, apoptosis assay and animal experiments were performed.
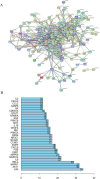
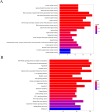
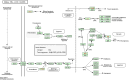
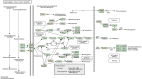
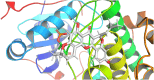
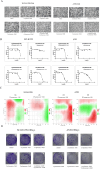
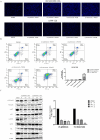
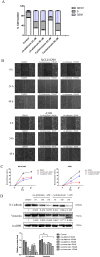
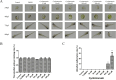
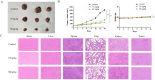
Results: 32 active ingredients and 434 targets of Chinese medicine cortex mori were obtained. Totally 2,3107 lung cancer related targets were collected, and 163 Chinese medicine-disease targets were derived from the intersection. The regulatory network of Chinese medicine-active ingredient-disease-targets showed that cortex mori acted on 163 disease targets of lung cancer mainly by cyclomolorusin, kuwanon D and Moracin A, etc. The core genes involving cortex mori treating lung cancer might consist of JUN, AKT1, etc. The core targets involved 162 biological processes, mainly including nuclear receptor activity, ligand-actived transcription factor activity, etc. The core study targeted 160 pathways, including AGE-RAGE signaling pathways associated with diabetes complications, fluid stress and atherosclerosis. Biologic cytological experiments showed that the effective active component cyclomorusin inhibited proliferation, inhibited migration and induced apoptosis of lung cancer through AKT-PI3K pathway. In vivo antitumor assay demonstrated that cyclomolorusin suppressed the tumor growth in mice.
Discussion: Cortex mori acts on AKT and other related disease targets of lung cancer cells through effective components such as cyclomolorusin, and plays a role in the treatment of lung cancer by inhibiting the signaling pathway associated with lung cancer occurrence and development.
Keywords: cortex mori; lung cancer; mechanism of action; network pharmacology; pathway; target.
Copyright © 2025 Shao, Yang, He, Zhang, Han, Xie, He and Hong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Minato H, Katayanagi K, Kurumaya H, Tanaka N, Fujimori H, Tsunezuka Y, et al. Verification of the eighth edition of the UICC-TNM classification on surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma: Comparison with previous classification in a local center. Cancer Rep. (2021) 5:e1422. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1422 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Min TR, Park HJ, Park MN, Kim B, Park SH. The Root Bark of Morus alba L. Suppressed the Migration of Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Inhibition of Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transition Mediated by STAT3 and Src. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:2244. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092244 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

