Effect of neuroinflammation on the progression of Alzheimer's disease and its significant ramifications for novel anti-inflammatory treatments
- PMID: 40510290
- PMCID: PMC12159511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.05.005
Effect of neuroinflammation on the progression of Alzheimer's disease and its significant ramifications for novel anti-inflammatory treatments
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is increasingly recognized as a disorder not solely of amyloid and tau accumulation but also of chronic immune dysregulation. Emerging evidence highlights the critical role of neuroinflammation, characterized by sustained activation of microglia and astrocytes, cytokine release, and inflammasome activation in accelerating AD progression. Genome-wide studies have further identified key inflammatory genes and immune pathways associated with increased disease risk. This review critically evaluates the mechanistic underpinnings of neuroinflammation in AD, focusing on glial cell behavior, immune signaling, and their contribution to neuronal dysfunction. Importantly, the review highlights recent advances in anti-inflammatory therapeutic approaches, including modulators of IL-1β, TNF-α, TREM2, and CB2 pathways. By integrating mechanistic and therapeutic insights, this work underscores the potential of immunomodulatory strategies as viable interventions in AD and provides a novel framework for future research in targeted anti-neuroinflammatory treatments.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Anti-inflammatory therapy; Cytokines; Glial cells; Microglia; Neuroinflammation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
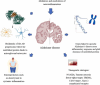
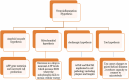
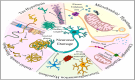


References
-
- Abdel-Aal R.A., Hussein O.A., Elsaady R.G., Abdelzaher L.A. Naproxen as a potential candidate for promoting rivastigmine anti-Alzheimer activity against aluminum chloride-prompted Alzheimer’s-like disease in rats; neurogenesis and apoptosis modulation as a possible underlying mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022;915 (Jan) - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Aal R., Hussein O., Elsaady R., Abdelzaher L. Celecoxib effect on rivastigmine anti-Alzheimer activity against aluminum chloride-induced neurobehavioral deficits as a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease; novel perspectives for an old drug. J. Med. Life Sci. 2021;0(0):44–82. Dec 24.
-
- Azargoonjahromi A. Dual role of nitric oxide in Alzheimer’s disease. Nitric Oxide. 2023;134–135:23–37. (May) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
