Optimization of Retrospective Gated-ECG Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography by Dose Reduction in Patients with Different Body Mass Indexes
- PMID: 40510307
- PMCID: PMC12153491
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2209-1537
Optimization of Retrospective Gated-ECG Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography by Dose Reduction in Patients with Different Body Mass Indexes
Abstract
Background: The reduction of patient radiation dose in coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) with acceptable image quality is considered an important factor in the research.
Objective: This study aims to optimize the CCTA protocol using a retrospective Electrocardiogram (ECG)-gated axial scan protocol in patients with different Body Mass Indexes (BMIs).
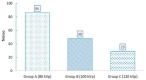
Material and methods: In this cross-sectional study, 66 patients into three main groups: 80 kVp (Group A), 100 kVp (Group B), and 120 kVp (Group C), underwent CCTA. Each group was then divided into two subgroups of BMI<25 and >25 kg/m2. Image noise, mean vascular attenuation at the aorta, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR) at five regions of coronary arteries, in which Coronary artery anomalies are common were qualitatively evaluated by subjective image quality analysis.
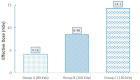
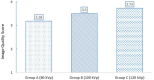
Results: At each kVp, there were no significant differences in CNR, SNR, noise level, and the effective dose between BMI>25 kg/m2 and BMI<25 kg/m2. The effective radiation dose of groups A, B, and C were 4.16, 8.46, and 14.3 mSv, respectively. Subjective image quality assessment scores were 3.18, 3.5, and 3.73 out of 4 in groups A, B, and C, respectively.
Conclusion: Patient radiation dose using retrospective ECG-gated CCTA can be reduced by about 70% at 80 kVp, which is almost close to the prospective CCTA dose ranges. The retrospective CCTA at 80 kVp can be optimized even in overweight patients (BMI>25 kg/m2).
Keywords: Computed Tomography Angiography; Effective Radiation Dose; Electrocardiography; Low Dose CT Angiography; Radiation Dosage; Retrospective Computed Tomography Angiography; Tube Voltage Reduction.
Copyright: © Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Meinel FG, Schoepf UJ, Townsend JC, Flowers BA, Geyer LL, Ebersberger U, et al. Diagnostic yield and accuracy of coronary CT angiography after abnormal nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27347-8. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maurya VK, Ravikumar R, Sharma P, Agrawal N, Bhatia M. Coronary CT angiography: A retrospective study of 220 cases. Med J Armed Forces India. 2016;72(4):377–83. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2016.03.008. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Meyersohn NM, Wood MJ, Steigner ML, Blankstein R, Ghoshhajra BB, Hedgire SS. Role of Coronary CT Angiography in Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020;2(6):e200364. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200364. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deseive S, Chen MY, Korosoglou G, Leipsic J, Martuscelli E, Carrascosa P, et al. Prospective Randomized Trial on Radiation Dose Estimates of CT Angiography Applying Iterative Image Reconstruction: The PROTECTION V Study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8(8):888–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.02.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sabarudin A, Siong TW, Chin AW, Hoong NK, Karim MKA. A comparison study of radiation effective dose in ECG-Gated Coronary CT Angiography and calcium scoring examinations performed with a dual-source CT scanner. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):4374. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40758-5. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
