Immunological biomarkers and gene signatures predictive of radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40510341
- PMCID: PMC12159018
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574113
Immunological biomarkers and gene signatures predictive of radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: A significant challenge in treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is its inherent resistance to radiation therapy, leading to poor patient prognosis. This study aimed to identify key genes influencing radiotherapy resistance in NSCLC through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis.
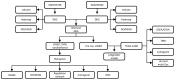
Methods: A total of 103 common genes were identified, enriched in critical biological pathways such as coagulation, complement activation, growth factor activity, and cytokine signaling. Using advanced machine learning techniques like SVM-RFE, LASSO regression, and random forest algorithms, four pivotal genes-TGFBI, FAS, PTK6, and FA2H-were identified.
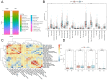
Results: TGFBI showed the strongest correlation with NSCLC prognosis as indicated by a diagnostic nomogram. Additionally, significant differences in immune cell infiltration, particularly involving naive B cells and M0 macrophages, were noted between high-risk and low-risk patients.
Discussion: The study suggests that targeting pathways regulating macrophage polarization or enhancing naive B cell activation could play a crucial role in addressing radiotherapy resistance. The findings highlight the potential therapeutic targets, thereby advancing the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying radiotherapy resistance in NSCLC, with implications for improving patient management and outcomes.
Keywords: NSCLC; bioinformatic analysis; bioinformatics analysis; immunological biomarkers; radiotherapy resistance.
Copyright © 2025 Lv, Yu, Xiong, Dai, Hu, Pan, Yue and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Construction of a novel radioresistance-related signature for prediction of prognosis, immune microenvironment and anti-tumour drug sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2447930. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2447930. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39797413 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Prognostic Value Exploration of Radiotherapy Sensitivity-Associated Genes in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Sep 2;2021:5963868. doi: 10.1155/2021/5963868. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34518802 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miRNAs in predicting radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11927-11936. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5052-8. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27075472 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic pathway activation and immune microenvironment features in non-small cell lung cancer: insights from single-cell transcriptomics.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1546764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546764. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40092988 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-486: a dual-function biomarker for diagnosis and tumor immune microenvironment characterization in non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2025 May 19;18(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12920-025-02158-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40390034 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

