Poplar: a phylogenomics pipeline
- PMID: 40510372
- PMCID: PMC12159734
- DOI: 10.1093/bioadv/vbaf104
Poplar: a phylogenomics pipeline
Abstract
Motivation: Generating phylogenomic trees from the genomic data is essential in understanding biological systems. Each step of this complex process has received extensive attention and has been significantly streamlined over the years. Given the public availability of data, obtaining genomes for a wide selection of species is straightforward. However, analyzing that data to generate a phylogenomic tree is a multistep process with legitimate scientific and technical challenges, often requiring a significant input from a domain-area scientist.
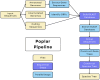
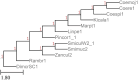
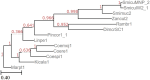
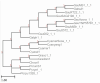
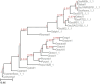
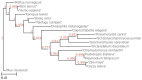
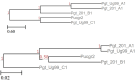
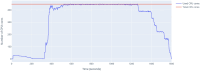
Results: We present Poplar, a new, streamlined computational pipeline, to address the computational logistical issues that arise when constructing the phylogenomic trees. It provides a framework that runs state-of-the-art software for essential steps in the phylogenomic pipeline, beginning from a genome with or without an annotation, and resulting in a species tree. Running Poplar requires no external databases. In the execution, it enables parallelism for execution for clusters and cloud computing. The trees generated by Poplar match closely with state-of-the-art published trees. The usage and performance of Poplar is far simpler and quicker than manually running a phylogenomic pipeline.
Availability and implementation: Freely available on GitHub at https://github.com/sandialabs/poplar. Implemented using Python and supported on Linux.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990;215:403–10. - PubMed
-
- Assembly. Accession No. GCF_000004695.1, Dictyostelium discoideum. National Library of Medicine (US): National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2009. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCF_000004695.1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

