Association between physiological serum total bilirubin concentrations and the progression of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 40510475
- PMCID: PMC12158686
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1588568
Association between physiological serum total bilirubin concentrations and the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze the relationship between physiological serum total bilirubin (STB) concentrations and the progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN).
Methods: The clinical features and pathological data of 159 patients with diabetic nephropathy confirmed by renal biopsy were retrospectively analyzed. They were divided into low bilirubin group (80 cases) and high bilirubin group (79 cases) according to the median of STB level. Clinical and pathological data of the two groups were collected and compared. The patients were followed up from the date of renal biopsy to June 30, 2024. Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test was used to perform survival analysis. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression risk model were used to analyze the risk factors of diabetic nephropathy. A restricted cubic spline model was used to show the nonlinear association between STB and DN.
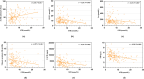
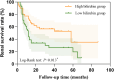
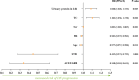
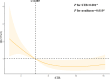
Results: When compared with physiologically high bilirubin group, patients in low bilirubin group might had higher level of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, 24h urinary protein, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR), fibrinogen (Fib) and higher rate of K-W nodules, renal tubular atrophy, renal interstitial inflammation and lower level of eGFR, hemoglobin, PLT, suggesting that low bilirubin group had more severe indicators. Spearman correlation analysis showed that STB was positive associated with eGFR (r = 0.270, P < 0.001) while negative associated with serum BUN (r = -0.236, P = 0.003), serum creatinine(r=-0.256, P < 0.001), 24h urine protein(r = -0.257, P < 0.001), UACR (r = -0.287, P < 0.001) and Fib (r = -0.398, P < 0.001). The Kaplan Meier analysis revealed that high STB had a higher possibility of renal survival rate when compared with lower STB (P = 0.013). After univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, STB (HR = 0.445, P = 0.001), hemoglobin (HR = 0.983, P = 0.002), age (HR = 0.977,P = 0.033) and ACEI/ARB (HR = 0.340, P = 0.001) were independently protective factors for the DN progression, while serum creatinine (HR = 1.003, P =0.001), 24h urine protein (HR = 1.088, P = 0.005) and cholesterol (HR = 1.104, P = 0.002) were risk factors for DN progression. The restricted cubic spline model showed that there was a significant nonlinear association between DN progression and STB level when it was less than 6.085 µmol/L.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that STB may serve as a potential biomarker for the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Lower STB levels may help identify high-risk patients who could benefit from earlier or more intensive interventions to slow disease progression.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; progression; restricted cubic spline; risk factor; serum total bilirubin.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Fang, Lin, Zhuo, Wan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
THE ASSOCIATION OF SERUM BILIRUBIN ON KIDNEY CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND RENAL OUTCOME IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: A BIOPSY-BASED STUDY.Endocr Pract. 2019 Jun;25(6):554-561. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0560. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Endocr Pract. 2019. PMID: 30865534
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index as an independent risk factor for diabetic nephropathy: a retrospective, single-center study.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 18;12:e18493. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18493. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39677959 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary renal tubular epithelial cells and casts as predictors of renal outcomes in patients with biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy.J Nephrol. 2024 Nov;37(8):2233-2242. doi: 10.1007/s40620-024-01995-8. Epub 2024 Jul 20. J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39031241
-
Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2749-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons learned from studies of the natural history of diabetic nephropathy in young type 1 diabetic patients.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008 Aug;5 Suppl 4:958-63. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18806710 Review.
References
-
- Chan KH, O’Connell RL, Sullivan DR, Hoffmann LS, Rajamani K, Whiting M, et al. Plasma total bilirubin levels predict amputation events in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) study. Diabetologia. (2013) 56:724–36. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2818-4 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

