Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification identify mitochondrial gene Dgat2 as a novel therapeutic biomarker for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
- PMID: 40510478
- PMCID: PMC12159077
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1539646
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification identify mitochondrial gene Dgat2 as a novel therapeutic biomarker for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
Abstract
Background: Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a severe disease marked by high morbidity and mortality, often exacerbated by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MI/RI). Mitochondrial metabolism plays a critical role in MI/RI progression. This study aimed to identify potential new targets and biomarkers for mitochondria-related genes in MI/RI.
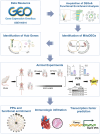
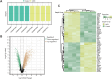
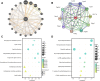
Methods: MI/R microarray data (GSE160516) from the GEO database and a mitochondrial geneset were analyzed. Limma identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs), followed by GSEA, GO, and KEGG pathway enrichment. Mitochondria-related DEGs (MitoDEGs) were pinpointed. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) networks and machine learning identified key MitoDEGs. Regulatory networks were constructed using transcription factor (TF) predictions. Immune cell infiltration was assessed with ImmuCelAl, and correlations between MitoDEGs and immune cell levels were examined. Mouse myocardial ischemia-reperfusion models were established to validate pivotal MitoDEGs.
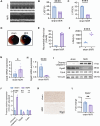
Results: MitoDEGs were enriched in bio-oxidation, immune-inflammation, and oxidative stress pathways. Machine learning identified two hub genes: Dgat2 and Cybb. Dgat2 was significantly elevated in ischemia-reperfusion mouse models, confirmed by RT-PCR and Western blot. Functional enrichment indicated that Dgat2 may be involved in biological oxidation and lipid metabolism. TF prediction suggested PPARG as a regulator of Dgat2 expression. Immune infiltration analysis revealed significant correlations between Dgat2 and immune cells, including CD4_T_cells and NK cells, suggesting a role for immunity in MI/RI.
Conclusions: We found that Dgat2 could be exploited as a novel mitochondria-related gene target and biomarker in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, which is of great clinical significance.
Keywords: Dgat2; bioinformatics analysis; mitochondria; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zhou, Xue, Yin, Liu, Wu, Zhao, An and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that the study was done without any commercial or financial links that could be seen as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Jennings RB, Steenbergen C, Jr., Reimer KA. Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Monogr Pathol. (1995) 37:47–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

