Differentially expressed ncRNAs as key regulators in infection of human bronchial epithelial cells by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant
- PMID: 40510596
- PMCID: PMC12162024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102559
Differentially expressed ncRNAs as key regulators in infection of human bronchial epithelial cells by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant
Abstract
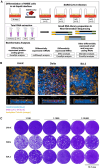
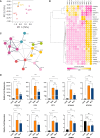
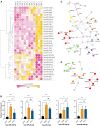
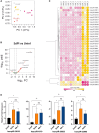
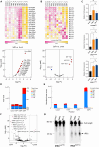
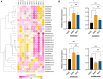
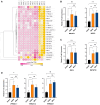
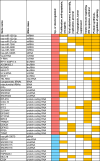
SARS-CoV-2 infection initiates complex interactions at mucosal barriers. In primary human bronchial epithelial cells, we investigated changes in the small RNA transcriptome induced by Delta variant infection. Thereby, we uncovered differential expression of a specific set of microRNAs (miRNAs), PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), vault RNAs, Y RNAs, and long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs), which inhibit apoptosis while promoting cell proliferation and viral infection. Conversely, differential expression of 7SL, U2, and RPPH1 RNAs, as well as miR-155-5p and miR-27a-5p, was found to be involved in antiviral signaling. In addition, expression of the protein-coding genes CXCL10, IFIT1, NCOA7, IFIT2, SIX3, and RPSA was increased during infection. Interestingly, the ribosomal protein RPSA has recently been reported to also serve as a viral surface receptor promoting pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling. By investigating these differentially expressed genes also after Omicron BA.2 variant infection, we observed a significantly lower expression of the protein-coding genes CXCL10, IFIT2, and ZC3HAV1. In contrast, expression changes for the majority of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) were similar between Delta and Omicron variants with the exception of miR-155-5p and 5'-tRFGlu(TTC), emphasizing their potential as biomarkers for disease severity. Our findings thus highlight distinct molecular responses in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, revealing specific genes and ncRNAs involved in viral replication, immune response, and apoptosis.
Keywords: MT: Non-coding RNAs; SARS-CoV-2; non-coding RNAs; pathways; transcriptomic profile; virus variants.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

