Multiple strategies were adopted to optimize the enzymatic characteristics and improve the expression of bovine chymosin BtChy in Kluyveromyces lactis for cheese production
- PMID: 40510666
- PMCID: PMC12158995
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605229
Multiple strategies were adopted to optimize the enzymatic characteristics and improve the expression of bovine chymosin BtChy in Kluyveromyces lactis for cheese production
Abstract
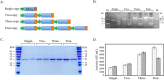
Chymosin (EC3.4.23.4), primarily sourced from calf abomasum, serves as a conventional coagulant in milk curdling during cheese production. To improve the enzymatic properties and enhance the expression of calf chymosin (BtChy) in Kluyveromyces lactis to meet the demands of the cheese industry, the in silico engineering via hotspot scanning and molecular dynamics analysis was adopted. This approach improved the activity of BtChy on milk curdling and increased its sensitivity at 65°C. Multiple strategies were utilized to develop an environmentally friendly method for chymosin production. These included screening for constitutive promoters and signal peptides, as well as in vitro construction of a concatemer of the BtChy gene. The optimal combination, comprising the PTDH3 promoter, invertase signal peptide, and a four-copy BtChy gene integrated into the yeast genome, was identified. After high-density cultivation in a 5-L bioreactor, the recombinant yeast achieved an activity of 42,000 SU/mL, a 52.5-fold increase over the original wild-type chymosin gene.
Keywords: calf chymosin; gene dosage; in silico engineering; promoter; signal peptide.
Copyright © 2025 Han, Zhang, Rao, Lei and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Enhanced production of recombinant calf chymosin in Kluyveromyces lactis via CRISPR-Cas9 engineering.Bioresour Technol. 2025 Mar;419:132116. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2025.132116. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Bioresour Technol. 2025. PMID: 39863179
-
[Construction of a Kluyveromyces lactis strain with multi-copy integration for enhanced bovine chymosin production by CRISPR/Cas9 and UV mutagenesis].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024 Sep 25;40(9):2983-2997. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240183. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39319719 Chinese.
-
[Gene synthesis of the bovine prochymosin gene and high-level expression in Kluyvermyces lactis].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010 Sep;26(9):1281-6. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21141120 Chinese.
-
Chymosin and other milk coagulants: sources and biotechnological interventions.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2010 Dec;30(4):243-58. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2010.483459. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20524840 Review.
-
Advances in research on calf rennet substitutes and their effects on cheese quality.Food Res Int. 2021 Nov;149:110704. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110704. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34600696 Review.
References
-
- Agrawal R., Punarva H. B., Heda G. O., Vishesh Y. M., Karunakar P. (2024). Vina Lig gen: a method to generate Lig plots and retrieval of hydrogen and hydrophobic interactions from protein-ligand complexes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 42, 12040–12043. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2266524, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

