Three-dimensional reconstruction of cone beam CT scan in the planning of the surgery of mandibular impacted third molars
- PMID: 40510718
- PMCID: PMC12156845
- DOI: 10.4103/njms.njms_135_22
Three-dimensional reconstruction of cone beam CT scan in the planning of the surgery of mandibular impacted third molars
Abstract
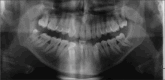
Objectives: The aim of this work is to evaluate the possibility that the three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan may facilitate the technical planning of the surgical extraction of third molars, whose roots are located in proximity of or in contact with the inferior alveolar nerve.
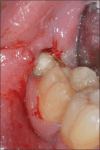
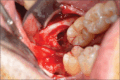
Materials and methods: This article describes the planning process and the extraction of a lower third molar with the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) entrapped through its roots using the 3D reconstruction of a CBCT scan.
Results: After-surgery clinical examinations showed normal healing of the surgical wound and no neurological symptoms.
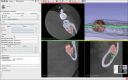
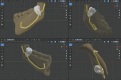
Conclusions: The 3D reprocessing of a CBCT allows the construction of a computer-aided design model to investigate the spatial relationships between the wisdom tooth and the IAN. This method makes it possible to reconstruct a virtual model to preview the tooth and its spatial relationships, simplifying the mental processes of reworking and analyzing the existing relationships in the area, an important aid, especially in cases that are difficult to diagnose with a first-level examination. Indeed, it helps in reducing the risk of intra-operative injury to the nerve during extraction procedures.
Keywords: Impacted third molar; inferior alveolar nerve; neurological lesion; pre-operative surgical planning; three-dimensional surgical planning.
Copyright: © 2025 National Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ghaeminia H, Meijer GJ, Soehardi A, Borstlap WA, Mulder J, Vlijmen OJ, et al. The use of cone beam CT for the removal of wisdom teeth changes the surgical approach compared with panoramic radiography: A pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40:834–9. - PubMed
-
- de Toledo Telles-Araújo G, Peralta-Mamani M, Caminha RDG, de Fatima Moraes-da-Silva A, Rubira CMF, Honório HM, et al. CBCT does not reduce neurosensory disturbances after third molar removal compared to panoramic radiography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24:1137–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
