Epidemiological characteristics of adenovirus in children in Yancheng, China, 2023-2024
- PMID: 40510801
- PMCID: PMC12158925
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1587257
Epidemiological characteristics of adenovirus in children in Yancheng, China, 2023-2024
Abstract
Objective: To understand the epidemiology and evolutionary characteristics of human adenovirus (HAdV) infecting children in Yancheng, China, during the winter of 2023-2024.
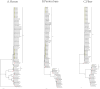
Methods: HAdV-positive throat swab samples were collected from pediatric patients in Yancheng. The Hexon, Penton base, and Fiber genes were amplified and sequenced for typing and phylogenetic analysis of HAdV.
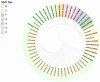
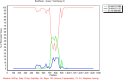
Results: 170 HAdV-positive samples were collected and identified from children with acute respiratory infection (ARI) in Yancheng. A total of 133 samples were successfully amplified and sequenced for Hexon, Penton base, and Fiber genes. Phylogenetic analysis showed that HAdV-B3 was the dominant circulating strain, and two strains of B21, one strain of C1 and one strain of C5 were also identified.
Conclusion: During the winter of 2023-2024, HAdV infecting children in Yancheng was mainly the B3 type.
Keywords: adenovirus; epidemiological characteristics; genetic features; phylogenetic trees; respiratory infections.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Cao, Qu, Tian, Shen, Liu, Luo, Song, Wen, Xue, Hu, Shi, Zhang, Zhu, Song and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis between genotypes of adenovirus isolates from hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infections and clinical manifestations in Wuhan, China, from June 2022 to September 2023.Virol Sin. 2025 Feb;40(1):50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.12.004. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39710326 Free PMC article.
-
Human adenovirus type 4 (HAdV-4) associated acute respiratory tract infection in children & genetic characteristics of HAdV-4 in China: a prospective multicenter study.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 9;24(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09835-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39251906 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological, clinical, and molecular analysis of human adenovirus infections in hospitalized children with acute respiratory infections in Tianjin, China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 14;15:1600990. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1600990. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40727707 Free PMC article.
-
High-incidence of human adenoviral co-infections in taiwan.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 20;8(9):e75208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075208. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24073254 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High-Frequency Recombination of Human Adenovirus in Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Infections in Beijing, China.Viruses. 2024 May 23;16(6):828. doi: 10.3390/v16060828. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avendaño Carvajal L., Perret Pérez C. (2020). Epidemiology of Respiratory Infections. Pediatric Respiratory Diseases 1, 263–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26961-6_28 - DOI
-
- Brini I., Guerrero A., Ezzine I. K., Höller D. O., Hetzer B., Würzner R., et al. (2020). Human adenoviruses associated with respiratory illness in neonates, infants, and children in the Sousse area of Tunisia. J. Med. Virol 6, 145–151. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26375 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

