Mechanosensitive nuclear checkpoint: nuclear envelope as a sensor of chromosomal instability and driver of cell fate
- PMID: 40510846
- PMCID: PMC12162011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbm.2025.100135
Mechanosensitive nuclear checkpoint: nuclear envelope as a sensor of chromosomal instability and driver of cell fate
Abstract
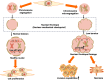
The nuclear envelope (NE) is a dynamic, mechanosensitive structure that functions as a protective barrier for the genome and serves as a checkpoint responding to external stimuli. It plays a critical role in maintaining genomic stability and regulating cell fate. This review synthesizes recent research highlighting the role of NE as a mechanical checkpoint in ensuring accurate chromosome segregation, regulating cell cycle progression, and contributing to cancer development. Chromosome mis-segregation during cell division is a major driver of aneuploidy, a condition closely associated with genomic instability and cellular transformation. The role of NE in chromatin organization and gene expression regulation is also discussed, underscoring its importance in cell differentiation and identity.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Chromatin; Gene expression; Mechanosensitive checkpoint; Nuclear envelope.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosome mis-segregation triggers cell cycle arrest through a mechanosensitive nuclear envelope checkpoint.Nat Cell Biol. 2025 Jan;27(1):73-86. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01565-x. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39779939 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome Segregation in Closed Mitosis Under an Excess of Nuclear Envelope.Biol Cell. 2025 May;117(5):e70011. doi: 10.1111/boc.70011. Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40391723 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced genomic instabilities caused by deregulated microtubule dynamics and chromosome segregation: a perspective from genetic studies in mice.Carcinogenesis. 2009 Sep;30(9):1469-74. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp081. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19372138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer biology and the nuclear envelope: a convoluted relationship.Semin Cancer Biol. 2013 Apr;23(2):125-37. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013. PMID: 22311402 Review.
-
Suppression of genomic instabilities caused by chromosome mis-segregation: a perspective from studying BubR1 and Sgo1.J Formos Med Assoc. 2009 Dec;108(12):904-11. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(10)60002-2. J Formos Med Assoc. 2009. PMID: 20040454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ungricht R., Kutay U. Mechanisms and functions of nuclear envelope remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(4):229–245. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Jiménez N., Pradillo M. The role of the nuclear envelope in the regulation of chromatin dynamics during cell division. J Exp Bot. 2020;71(17):5148–5159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

