Efficient Electrochemical Reforming of Water-Insoluble C‑Only Plastic Wastes
- PMID: 40510916
- PMCID: PMC12153041
- DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5c00907
Efficient Electrochemical Reforming of Water-Insoluble C‑Only Plastic Wastes
Abstract
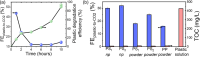
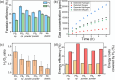
We report here the efficient electrochemical reforming of hydrocarbon polymer wastes, i.e. composed of C-C and C-H bonds only, in aqueous solution at 3 V. Anodic degradation of these chemically resilient wastes is achieved with Faradaic efficiencies of up to 32% on a Ni/Sb-doped SnO2 electrode. The hydrophobic plastic particles, initially present as large aggregates, are solubilized during the early stages of the reaction, which is essential to achieve high reforming efficiencies. Cathodic H2 generation is demonstrated with Faradaic and energy efficiencies of up to 57% and 30%, respectively. Under optimized conditions, electroreforming requires ca. 0.10 kWh/g of plastic degraded, which is >120 times more efficient than that previously reported on boron-doped diamond anodes. If scaled up, energy costs as low as ca. 2000$/ton could be achieved, while the H2 generated could cover up to ca. 70% of these costs. CO2 emissions, expected to be ranging from 1.65 to 13.02 kgCO2eq/kgH2, are competitive with conventional plastic-to-H2 high-temperature processes. Our results support the industrial potential of plastic electroreforming to efficiently treat chemically resilient plastic wastes.
Keywords: electrocatalysis; hydrogen; plastic waste; polypropylene; polystyrene; reforming.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electroreforming of plastic wastes for value-added products.Chem Commun (Camb). 2024 Dec 17;61(1):33-45. doi: 10.1039/d4cc04574b. Chem Commun (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39601665 Review.
-
Electroreforming of Biomass for Value-Added Products.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Nov 16;12(11):1405. doi: 10.3390/mi12111405. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Low-temperature Hydrogen Production by Electrochemical-assisted Methanol Steam Reforming.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2024 Feb 12;63(7):e202315157. doi: 10.1002/anie.202315157. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2024. PMID: 38143245
-
A sustainable solar-driven electrochemical process for reforming lignocellulosic biomass effluent into high value-added products: green hydrogen, carboxylic and vanillic acids.RSC Adv. 2023 Dec 11;13(50):35755-35765. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05772k. eCollection 2023 Nov 30. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38090624 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing 2D materials to enhance H2 generation efficiency via photocatalytic reforming industrial and solid waste.Environ Res. 2021 Sep;200:111239. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111239. Epub 2021 May 14. Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 33992636 Review.
References
-
- OECD . https://www.oecd.org/environment/plastics/increased-plastic-leakage-and-...Accessed 2022–08–18.
-
- On the plastics crisis. Nature Sustainability. 2023, 6 (10), 1137–1137. 10.1038/s41893-023-01236-z. - DOI
-
- Chamas A., Moon H., Zheng J., Qiu Y., Tabassum T., Jang J. H., Abu-Omar M., Scott S. L., Suh S.. Degradation Rates of Plastics in the Environment. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020;8(9):3494–3511. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06635. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
