Perceived stress and sleep quality in young and middle-aged patients with coronary heart disease: the mediating role of perceived social support and mental health literacy
- PMID: 40510930
- PMCID: PMC12159011
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1444831
Perceived stress and sleep quality in young and middle-aged patients with coronary heart disease: the mediating role of perceived social support and mental health literacy
Abstract
Background: Globally, there is an increasing emphasis on mental health, particularly its role in the recovery of patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Although previous studies have shown that perceived social support (PSS), mental health literacy (MHL), perceived stress and sleep quality are significantly related, the interaction mechanism remains unclear.
Objectives: To explore the status of perceived stress, sleep quality, PSS and MHL in young and middle-aged patients with CHD and to test the mediating effect of PSS and MHL between perceived stress and sleep quality.
Methods: A convenience sample of 183 young and middle-aged patients with CHD was enrolled between September 2023 and January 2024. Data were collected using a demographic characteristics questionnaire, the mental health literacy scale, the perceived social support scale, the Chinese perceived stress scale, and the Athens insomnia scale. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to examine relationships between variables, while linear regression analysis was used to assess the predictive effects of perceived stress, PSS, and MHL on sleep quality. Additionally, the PROCESS 4.2 macro for SPSS was employed to explore the mediating roles of PSS and MHL in the relationship between patients' perceived stress and sleep quality.
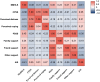
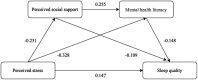
Results: Correlation analysis revealed that perceived stress in young and middle-aged patients with CHD was negatively correlated with MHL (r = -0.381, p < 0.001) and PSS (r = -0.244, p < 0.001), but positively correlated with sleep quality (r = 0.349, p < 0.001). Additionally, the chain mediating role of PSS and MHL (3.93%) between perceived stress and sleep quality was significant.
Conclusion: Perceived stress not only directly affected sleep quality in young and middle-aged patients with CHD but also could indirectly affect sleep quality through PSS and MHL.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; mental health; sleep quality; social support; stress.
Copyright © 2025 Lu, Li, Cui, Zheng and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the mediating role of self-disclosure between mental health literacy and psychological distress: a cross-sectional study among HIV-positive young and middle-aged men who have sex with men in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Feb 13;15(2):e095735. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-095735. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39947831 Free PMC article.
-
Mental health literacy and help-seeking intention among Chinese elite athletes: the mediating roles of stigma and social support.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1332343. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1332343. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39328811 Free PMC article.
-
Low mental health literacy and its association with depression, anxiety and poor sleep quality in Chinese elderly.Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2022 Dec;14(4):e12520. doi: 10.1111/appy.12520. Epub 2022 Oct 9. Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36210054
-
The association of mental health literacy with mental well-being and help-seeking in young people: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Pediatr Nurs. 2023 Nov-Dec;73:e243-e250. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2023.09.017. Epub 2023 Sep 27. J Pediatr Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37775428
-
Association between perceived stress and depression among medical students during the outbreak of COVID-19: The mediating role of insomnia.J Affect Disord. 2021 Sep 1;292:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.028. Epub 2021 May 27. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 34107425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexim G. A., Rocha L. F., Dobri G. P., Rosa Junior A. D. S., Reis R. T. B., Nogueira A. C. C., et al. (2022). Clinical and economic impact of coronary artery bypass graft and percutaneous coronary intervention in young individuals with acute coronary syndromes and multivessel disease: a real-world comparison in a middle-income country. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:1000260. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1000260, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Du L., Cai J., Yu J., Chen X., Yang X., Xu X., et al. (2024). Relations between posttraumatic growth and fear of progression among Young and middle-aged primary brain tumor patients: the parallel mediating role of perceived social support and illness uncertainty. World Neurosurg. 184, e794–e802. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.02.048, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources