Study of Glutathione S-Transferase, its Isoenzyme (Pi) and Tumor Marker (CA15-3, HE4) in Breast Carcinoma Patients (Before and After Treatment)
- PMID: 40511180
- PMCID: PMC12156647
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1785_24
Study of Glutathione S-Transferase, its Isoenzyme (Pi) and Tumor Marker (CA15-3, HE4) in Breast Carcinoma Patients (Before and After Treatment)
Abstract
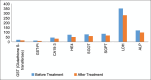
Breast carcinoma is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality among women. Breast cancer survival is highly reliant on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic and diagnostic roles of glutathione S-transferase (GST), its isoenzyme Pi (GST-Pi), and tumor markers CA15-3 and HE4 in breast cancer patients before and after treatment. The study was conducted on 311 breast carcinoma patients, recruited from Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Sawangi (Meghe), Wardha, and Datta Meghe Medical College, Nagpur. Blood samples were collected from each patient to estimate GST, GST-Pi, CA15-3, HE4, and liver enzymes (SGOT, SGPT, LDH, and ALP) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and fully automated biochemical analyzers. Results showed significant reductions in the levels of GST, GST-Pi, CA15-3, HE4, and liver enzymes post-treatment (P < 0.05), indicating a decrease in oxidative stress, drug resistance, tumor burden, and liver stress. Specifically, GST levels decreased from 20.5 ± 3.2 IU/L to 15.8 ± 2.7 IU/L, and CA15-3 levels dropped from 45.6 ± 10.1 U/mL to 32.4 ± 8.7 U/mL. These findings support the utility of these biomarkers in monitoring treatment response and disease progression in breast carcinoma patients. The study underscores the significance of GST, GST-Pi, CA15-3, HE4, and liver enzyme levels as valuable markers in the management of breast cancer, aiding in treatment monitoring and prognostication.
Keywords: Breast carcinoma; CA15-3; GST-Pi; HE4; diagnostic markers; glutathione S-transferase (GST); liver enzymes; oxidative stress.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study of Glutathione S-Transferase, Its Isoenzyme (Pi) and Tumor Marker (CA15-3, HE4) in Breast Carcinoma Patients (Before and After Treatment).J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 May;17(Suppl 1):S909-S912. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1792_24. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40511025 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Glutathione S-Transferase, Its Isoenzyme (Pi), and Tumor Markers (CA15-3, HE4) in Breast Carcinoma Patients (Before and After Treatment).J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 May;17(Suppl 1):S113-S116. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1790_24. Epub 2025 Apr 25. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40511194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimation of glutathione S-transferase and its Pi isoenzyme in tumor tissues and sera of patients with ovarian cancer.Anticancer Res. 2000 Mar-Apr;20(2B):1229-35. Anticancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10810426
-
Serum Human Epididymis Protein-4 (HE4) - A novel Approach to Differentiate Malignant Frombenign Breast Tumors.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Aug 1;22(8):2509-2507. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.8.2509. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34452565 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Markers and Their Diagnostic Significance in Ovarian Cancer.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;13(8):1689. doi: 10.3390/life13081689. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629546 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013.
-
- Moscow JA, Townsend AJ, Cowan KH. Elevation of pi class glutathione S-transferase activity in human breast cancer cells by transfection of the GST pi gene and its effect on sensitivity to toxins. Mol Pharmacol. 1989;36:22–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous