Predictive and prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40512416
- PMCID: PMC12165981
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01746-4
Predictive and prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
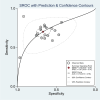
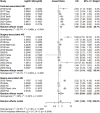
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been suggested as a potential biomarker for the prediction and risk stratification of acute kidney injury (AKI), but conflicting results were reported by literature. We therefore conducted a pooled analysis to consolidate available evidence regarding the predictive and prognostic value of NLR in AKI patients. A systematic search was performed in the PubMed/Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Central) databases from inception to March 2025 for cohort studies investigating the association between NLR and AKI. Quality assessment was performed via the Quality Assessment for Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy (QUADAS-2) tool. The predictive and prognostic value of the NLR for AKI was evaluated via pooled estimates of odds ratio (OR), sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NeLR), diagnostic score (DS), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves, and the Fagan nomogram. Twenty-nine studies with 102,870 patients were pooled in this meta-analysis. Higher NLR was associated an increased risk of AKI (OR 1.52, 95% CI 1.29-1.79; p < 0.001). The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.70 (95% CI 0.65-0.74) and 0.67 (95% CI 0.60-0.74). The combined values of the PLR, NeLR, DS, and DOR were 2.13 (1.74-2.60), 0.45 (0.38-0.52), 1.56 (1.24-1.89), and 4.78 (3.46-6.60), respectively, with a pooled area under the curve (AUC) for the SROC being 0.74 (95% CI 0.70-0.78). Subgroup analysis suggested that the associations remained statistically significant in contrast-associated AKI (p < 0.001) and surgery-associated AKI (p < 0.001), but of boarder line significance in sepsis-associated AKI (p = 0.082). In addition, higher NLR was also found to be related to 1.47-fold increase in mortality among AKI patients (OR 1.47, 95% CI 1.13-1.91, p = 0.004). NLR is not only an effective marker for predicting AKI event, but also a prognostic tool to identify AKI patients with higher risk of death. Future studies are needed to justify its value in different AKI subtypes.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Biomarker; Diagnosis; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2009 Dec;54(6):1012-24. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009. PMID: 19850388
-
The efficiency of blood cell counts and inflammatory indices in prediction of need for acute kidney injury in patients with crush syndrome.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 26;26(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04318-6. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40713512 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 5;19(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0794-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28057046 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of suPAR in AKI: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023 Jan;27(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10157-022-02300-2. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36469196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossiter A, La A, Koyner JL, et al. New biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024;61:23–44. - PubMed
-
- Wei W, Huang X, Yang L, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker of mortality and disease severity in septic acute kidney injury patients: a retrospective study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;116:109778. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Shao T, Wang J, et al. An update on potential biomarkers for diagnosing diabetic foot ulcer at early stage. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110991. - PubMed
-
- Huang Z, Fu Z, Huang W, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: a meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:641–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

