The sports nutrition knowledge of large language model (LLM) artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots: An assessment of accuracy, completeness, clarity, quality of evidence, and test-retest reliability
- PMID: 40512755
- PMCID: PMC12165421
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325982
The sports nutrition knowledge of large language model (LLM) artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots: An assessment of accuracy, completeness, clarity, quality of evidence, and test-retest reliability
Abstract
Background: Generative artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots are increasingly utilised in various domains, including sports nutrition. Despite their growing popularity, there is limited evidence on the accuracy, completeness, clarity, evidence quality, and test-retest reliability of AI-generated sports nutrition advice. This study evaluates the performance of ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude's basic and advanced models across these metrics to determine their utility in providing sports nutrition information.
Materials and methods: Two experiments were conducted. In Experiment 1, chatbots were tested with simple and detailed prompts in two domains: Sports nutrition for training and Sports nutrition for racing. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to assess interrater agreement and chatbot performance was assessed by measuring accuracy, completeness, clarity, evidence quality, and test-retest reliability. In Experiment 2, chatbot performance was evaluated by measuring the accuracy and test-retest reliability of chatbots' answers to multiple-choice questions based on a sports nutrition certification exam. ANOVAs and logistic mixed models were used to analyse chatbot performance.
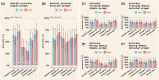
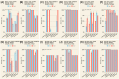
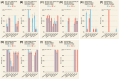
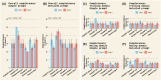
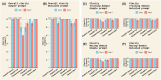
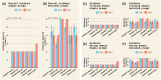
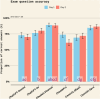
Results: In Experiment 1, interrater agreement was good (ICC = 0.893) and accuracy varied from 74% (Gemini1.5pro) to 31% (ClaudePro). Detailed prompts improved Claude's accuracy but had little impact on ChatGPT or Gemini. Completeness scores were highest for ChatGPT-4o compared to other chatbots, which scored low to moderate. The quality of cited evidence was low for all chatbots when simple prompts were used but improved with detailed prompts. In Experiment 2, accuracy ranged from 89% (Claude3.5Sonnet) to 61% (ClaudePro). Test-retest reliability was acceptable across all metrics in both experiments.
Conclusions: While generative AI chatbots demonstrate potential in providing sports nutrition guidance, their accuracy is moderate at best and inconsistent between models. Until significant advancements are made, athletes and coaches should consult registered dietitians for tailored nutrition advice.
Copyright: © 2025 Solomon, Laye. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
TS has given invited talks at societal conferences and university/pharmaceutical symposia for which the organisers paid for travel and accommodation; he has also received research money from publicly funded national research councils and medical charities, and private companies, including Novo Nordisk Foundation, AstraZeneca, Amylin, AP Møller Foundation, and Augustinus Foundation; and, he has consulted for Boost Treadmills, GU Energy, and Examine.com, and owns a consulting business, Blazon Scientific, and an endurance athlete education business, Veohtu. These companies have had no control over the research design, data analysis, or publication outcomes of this work. ML has given invited talks at societal conferences and university symposia and meetings for which the organisers paid for travel and accommodation; he has received research money from Augustinus Foundation, American College of Sports Medicine, and national research institutions; and, he has consulted for Zepp Health, Levels Health, GU Energy, and EAB labs, and has coached for Sharman Ultra Coaching. These companies have had no control over the research design, data analysis, or publication outcomes of this work. My Sports Dietitian provided a set of multiple-choice questions designed to resemble the Certified Specialist in Sports Dietetics (CSSD) board exam. Neither TPJS nor MJL have any financial relationships with My Sports Dietitian. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
-
- Grand View Research. Chatbot Market Size, Share & Trends, Analysis Report By Application (Customer Services, Branding & Advertising), By Type, By Vertical, By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America), And Segment Forecasts, 2023 - 2030. [cited 6 Sep 2024]. Available: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/chatbot-market
-
- Google. Google Trends for “ChatGPT”, “Microsoft Copilot”, “Gemini”, and “Claude”. [cited 6 Sep 2024]. Available: https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2022-01-01%202024-04-25&q=...
-
- AI Endurance. AI Endurance: AI running, cycling, and triathlon coach. [cited 20 Jan 2025]. Available: https://aiendurance.com/
-
- AlbonApp. Trail running training app. [cited 12 Dec 2024]. Available: https://www.albon.app/
-
- Vert.run. A training app for trail and ultrarunners. [cited 12 Dec 2024]. Available: https://vert.run/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

