Prognostic significance of receptor conversion following neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a systematic review & meta-analysis
- PMID: 40513473
- PMCID: PMC12198027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2025.104516
Prognostic significance of receptor conversion following neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a systematic review & meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Receptor conversion following neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer may influence prognosis and adjuvant treatment decisions. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the prognostic significance of changes in hormone receptor (HR) and HER2 status after neoadjuvant therapy.
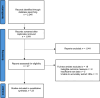
Methods: This study was performed in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. A systematic search of the literature was conducted to identify studies assessing the prognostic effect of receptor conversion after neoadjuvant treatment in breast cancer. Studies reporting receptor status before and after neoadjuvant therapy, with associated survival outcomes, were included. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) for disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated using random-effects models.
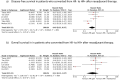
Results: Twenty-two studies (n = 5370) were included in this meta-analysis. HR gain demonstrated significantly improved DFS (HR 0.49, 95 % CI 0.25-0.97; p = 0.04), but no OS benefit. HR loss was associated with both significantly worse DFS (HR 3.42, 95 % CI 1.93-6.08; p < 0.001) and OS (HR 1.99, 95 % CI 1.04-3.84; p = 0.04). HER2 gain had a negative impact on DFS (HR 1.89, 95 % CI 1.00-3.58; p = 0.05), with no significant effect on OS. HER2 loss was associated with significantly poorer DFS (HR 1.92, 95 % CI 1.51-2.43; p < 0.001) and OS (HR 2.20, 95 % CI 1.44-3.38; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: This systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrates that receptor conversion following neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer significantly impacts survival outcomes. Specifically, gaining HR positivity is associated with improved DFS, while losing HR positivity correlates with worse DFS and OS. With regards to HER2, gaining positivity is associated with worse DFS, and losing positivity is associated with worse DFS and OS, compared to patients who maintain their initial status. These findings underscore the potential importance of reassessing receptor status after neoadjuvant therapy to tailor subsequent treatment decisions accurately.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2; Hormone receptor; Neoadjuvant therapy; Prognosis; Receptor conversion; Targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pathologic response rates in HER2-low versus HER2-zero early breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 15;27(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-01989-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40089780 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of loss of HER2 positivity following neoadjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients on long-term prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2025 Apr;135:102923. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2025.102923. Epub 2025 Mar 16. Cancer Treat Rev. 2025. PMID: 40112659
-
Efficacy and safety of different regimens of neoadjuvant therapy in patients with hormone receptor-positive, her2-negative breast cancer: a network meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1420214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1420214. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39247184 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 5;19(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0794-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28057046 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geyer C.E., Untch M., Huang C.-S., et al. Survival with trastuzumab emtansine in residual HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2025;392(3):249–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

