An ABCB11 variant registry and novel knockin mouse model of PFIC2 based on the clinically relevant ABCB11 E297G variant
- PMID: 40513781
- PMCID: PMC12273561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100840
An ABCB11 variant registry and novel knockin mouse model of PFIC2 based on the clinically relevant ABCB11 E297G variant
Abstract
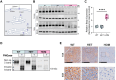
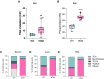
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 (PFIC2) is a rare pediatric cholestatic liver disease caused by genetic deficiency in the bile salt export pump (BSEP, ABCB11). BSEP is an ATP-binding cassette transporter and the primary regulator of hepatic bile acid efflux. Loss of BSEP function in PFIC2 leads to cholestasis and intrahepatic accumulation of bile acids, the native toxicity of which drives progressive liver injury, in a manner that correlates with ABCB11 genotype. Here, to support ongoing PFIC2 research, we present two novel translational tools, 1) a codified evidence-based catalog of published disease relevant ABCB11 mutations and 2) a knockin mouse model of the PFIC2-associated missense variant E297G. Using a combination of AI-based indexing of the literature and manual review, we identified 476 nonbenign ABCB11 variants in published patients with cholestatic disease, of which 240 were associated with PFIC2. Additionally, we present phenotypic validation of a novel knockin mouse model of the cholestasis-associated ABCB11 E297G variant. BsepE297G homozygous mice recapitulate the core molecular and pathophysiological aspects of PFIC2, including perturbed Bsep processing and membrane trafficking, cholestasis, and hepatotoxicity. Moreover, and consistent with clinical data, pharmacological ileal bile acid transporter inhibition improved the cholestatic phenotype of BsepE297G mice through increased fecal bile acid excretion. Together, these tools can support clinical and translational efforts to advance understanding and treatment of PFIC2.
Keywords: Abcb11; BSEP; PFIC2; bile acid; cholestasis; missense.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genotype-phenotype relationships of truncating mutations, p.E297G and p.D482G in bile salt export pump deficiency.JHEP Rep. 2022 Nov 16;5(2):100626. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100626. eCollection 2023 Feb. JHEP Rep. 2022. PMID: 36687469 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of plasma membrane expression in progressive and benign mutations of the bile salt export pump (Bsep/Abcb11) correlate with severity of cholestatic diseases.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):C1709-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00327.2007. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17855769
-
Maralixibat in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (MARCH-PFIC): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jul;9(7):620-631. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00080-3. Epub 2024 May 6. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38723644 Clinical Trial.
-
The Bile Salt Export Pump: Molecular Structure, Study Models and Small-Molecule Drugs for the Treatment of Inherited BSEP Deficiencies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 14;22(2):784. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020784. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and trafficking of the bile salt export pump, BSEP: therapeutic implications of BSEP mutations.Mol Aspects Med. 2014 Jun;37:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 15. Mol Aspects Med. 2014. PMID: 23685087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Byrne J.A., Strautnieks S.S., Ihrke G., Pagani F., Knisely A.S., Linton K.J., et al. Missense mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCB11 impair bile salt export pump processing and function or disrupt pre-messenger RNA splicing. Hepatology. 2009;49:553–567. - PubMed
-
- Strautnieks S.S., Bull L.N., Knisely A.S., Kocoshis S.A., Dahl N., Arnell H., et al. A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat. Genet. 1998;20:233–238. - PubMed
-
- van Wessel D.B.E., Thompson R.J., Gonzales E., Jankowska I., Sokal E., Grammatikopoulos T., et al. Genotype correlates with the natural history of severe bile salt export pump deficiency. J. Hepatol. 2020;73:84–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

