Impact of enhanced pain knowledge on core outcomes in fibromyalgia patients with high self-reported pain education needs: a target trial emulation using the DANFIB registry
- PMID: 40514059
- PMCID: PMC12164631
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005576
Impact of enhanced pain knowledge on core outcomes in fibromyalgia patients with high self-reported pain education needs: a target trial emulation using the DANFIB registry
Abstract
Objective: Relationships between patient education and long-term clinical outcomes are complex. This study used real-world data to evaluate the impact of improved pain knowledge on clinical outcomes in fibromyalgia patients.
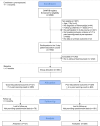
Methods: Prospectively collected registry-based observational data were analysed to emulate a randomised clinical trial. Study participants were diagnosed with fibromyalgia, had a high need to learn about pain (Numeric Rating Scale >7), had attended a 2-day therapeutic educational programme and re-rated their learning needs after the programme. A good educational outcome was defined as a re-rating score <5, while a poor outcome was ≥5. The primary endpoint at 9 months was the overall impact of fibromyalgia, measured by the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire Revised (FIQR) impact subscale.
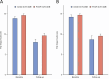
Results: The eligible cohort comprised 450 participants. The intention-to-treat from population included 121 participants (26.9%) with a good educational outcome and 329 participants (73.1%) with a poor educational outcome (comparator group). Missing outcome data were handled implicitly by the repeated measures linear mixed models, assuming data are missing at random.At the 9-month endpoint, the fully adjusted FIQR impact subscale score was lower in the good educational outcome group (8.0 (95% CI 7.3 to 8.7)) compared with the poor educational outcome group (9.6 (95% CI 9.0 to 10.2)), indicating a better clinical outcome for those with a good educational outcome. The model-estimated between-group difference was -1.6 (95% CI -2.5 to -0.7; p=0.0006) FIQR impact subscale units.
Conclusions: This study suggests that achieving pain educational learning objectives leads to better clinical outcomes in fibromyalgia patients, supporting the integration of pain education into patient programmes.
Keywords: Fibromyalgia; Health-Related Quality Of Life; Outcome and Process Assessment, Health Care; Pain; Rehabilitation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-management education programmes for osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 15;2014(1):CD008963. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008963.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24425500 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for treating fibromyalgia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD007070. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007070.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728665 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotics for fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 2;2016(6):CD011804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27251337 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 9;10(10):CD012172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012172.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28990665 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
