Interleukin-1β in circulating mononuclear cells predicts steatotic liver disease improvement after weight loss in subjects with obesity and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 40514652
- PMCID: PMC12164075
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02706-8
Interleukin-1β in circulating mononuclear cells predicts steatotic liver disease improvement after weight loss in subjects with obesity and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a major cardiovascular risk (CV) factor. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), a cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of obesity-associated inflammation and type 2 diabetes (T2D), promotes hepatic steatosis. The Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcome (CANTOS) trial showed that the inhibition of the IL-1β pathway was associated with a reduction of CV events in high-risk patients. The present study was designed to determine: (i) whether an equal degree of weight loss by liraglutide or lifestyle changes has a different impact on MASLD extent and IL-1β expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from obese subjects with prediabetes or early T2D; (ii) whether baseline IL-1β levels may predict the extent of weight loss and related metabolic changes.
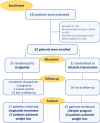
Methods: Thirty-two obese subjects with prediabetes (n = 16) or newly diagnosed T2D (n = 16), were randomized to the glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist (GLP1-RA) liraglutide or lifestyle counselling until achieving a comparable weight loss. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and gene expression of IL-1β in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were assessed by magnetic resonance and real time PCR, respectively.
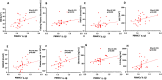
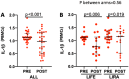
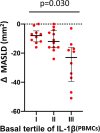
Results: At baseline, IL-1β was positively correlated to body mass index (BMI), fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, VAT, MASLD extent, platelet count, chemerin and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1-RA). After achievement of the weight loss target in the two groups, a significant but comparable reduction of IL-1β (p for difference = 0.56) was observed in both arms, in parallel with a comparable improvement in glycaemic control, C reactive protein (CRP), BMI and MASLD. Furthermore, basal IL-1β levels independently predicted the extent of MASLD decrease (p = 0.030); subjects in the highest tertile showed a median decrease of - 8.0 (95% CI - 12.3 to - 4.8) compared with - 23.0 (95% CI - 39.5 to - 16.3) in the lowest tertile.
Conclusion: In patients with obesity with initial impairment of glucose metabolism successful weight loss is associated with a reduction of both IL-1β levels and MASLD degree. Of interest, basal levels of IL-1β predict the extent of MASLD improvement, regardless of the intervention. Our results may set the stage for ad-hoc studies investigating the usefulness of baseline IL-1β a level as a drug-response biomarker.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Biomarker; Inflammation; Interleukin-1β; Liver disease; MASLD; Obesity; Prediabetes; Type 2 diabetes; Weight-loss.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The trial was approved by the Italian Ethics Committee of the University of Chieti (Approval n. 10 (protocol 20131) 23.05.2013). Each patient provided written informed consent before participation. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

