Transdermal delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated melanoma gene therapy via polyamines-modified thermosensitive hydrogels
- PMID: 40514654
- PMCID: PMC12164105
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03523-7
Transdermal delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated melanoma gene therapy via polyamines-modified thermosensitive hydrogels
Abstract
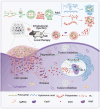
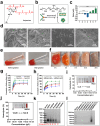
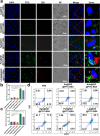
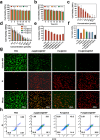
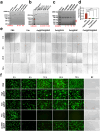
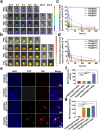
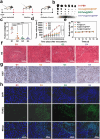
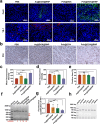
The main obstacles to the clinical application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system are off-target effects and low delivery efficiency. There is an urgent need to develop new delivery strategies and technologies. Three types of in situ injectable hydrogels with different electrical properties were created to find the most secure and efficient sustained-release drug delivery system. After in vitro and in vivo comparisons, we found that the positively charged hydrogels had higher cellular uptake, stronger gene editing efficiency, greater cytotoxicity, longer tumor accumulation, and better anti-tumor efficacy than negatively charged and neutral hydrogels. We designed single guide RNA targeting the Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) gene and then used it to create a ribonucleoprotein complex with Cas9 protein. Doxorubicin was co-encapsulated into this positively charged hydrogel to create a co-delivery system. By knocking down YB-1, the expression of YB-1 was reduced, inhibiting the growth and migration of melanoma cells. The strategy of combining YB-1 gene editing and intratumoral injection enhanced the therapeutic effect of doxorubicin while reducing side effects.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Hydrogel; Intratumoral injection; Polyamines; YB-1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal protocols adhered to institutional and local ethical regulations and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Hubei University (No.20240012, Hubei, China). Consent for publication: All authors agree for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A biodegradable lipid nanoparticle delivers a Cas9 ribonucleoprotein for efficient and safe in situ genome editing in melanoma.Acta Biomater. 2024 Dec;190:531-547. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.10.030. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39461690
-
Intratumoral Administration of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-Loaded with Norcantharidin Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 15;16:4073-4085. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S308057. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34163160 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin receptor-targeted polymeric nanoplatform for efficient CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to enhance synergistic hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Feb 20;23(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03214-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39979929 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targeting in Ovarian Cancer: Nano-Enhanced CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Drug Combination Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 30;20:3907-3931. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S507688. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40191042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome Editing for Disease Modeling and Therapy: Challenges and Opportunities for Nonviral Delivery.Chem Rev. 2017 Aug 9;117(15):9874-9906. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00799. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28640612 Review.
Cited by
-
The Collapse of Brain Clearance: Glymphatic-Venous Failure, Aquaporin-4 Breakdown, and AI-Empowered Precision Neurotherapeutics in Intracranial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 25;26(15):7223. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157223. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brody H. Gene therapy. Nature. 2018;564:S5. - PubMed
-
- Kozovska Z, Rajcaniova S, Munteanu P, Dzacovska S, Demkova L. CRISPR: history and perspectives to the future. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;141:111917. - PubMed
-
- van der Oost J, Patinios C. The genome editing revolution. Trends Biotechnol. 2023;41:396–409. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

