Proteomic analysis of hydrogen peroxide-treated human chondrocytes shows endoplasmic reticulum stress, cytoskeleton remodeling, and altered secretome composition
- PMID: 40514670
- PMCID: PMC12166578
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02291-z
Proteomic analysis of hydrogen peroxide-treated human chondrocytes shows endoplasmic reticulum stress, cytoskeleton remodeling, and altered secretome composition
Abstract
Background: Chondrocyte homeostasis is vital for maintaining the extracellular matrix (ECM) and overall cartilage health. In osteoarthritis (OA), for example, oxidative stress resulting from redox imbalances can disrupt chondrocyte homeostasis, leading to cartilage degradation. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a key mediator of oxidative stress and contributes to chondrocyte apoptosis and ECM degradation. Previous studies have explored individual protein responses to oxidative stress; however, a comprehensive proteomic analysis in chondrocytes has not been conducted. In this study, we aimed to assess the global proteomic alterations in chondrocytes exposed to H2O2 using a shotgun proteomics approach, which enables the detection of a broad spectrum of proteomic changes.
Methods: Chondrocytes were treated with H2O2 for 1, 4, and 16 h followed by protein extraction and processing, including denaturation, alkylation, and trypsin digestion. The peptides were then acidified, desalted, dried, and resuspended for LC-MS/MS. Proteomics data were analyzed using MaxQuant software to identify and quantify proteins. Secretome analysis was performed to examine protein secretion changes under oxidative stress. The statistical significance of all proteomics and secretome data was assessed using a two-tailed Student's t-test with a permutation-based FDR and an S0 parameter of 0.1 in the Perseus software. Other methods, including quantitative PCR, western blotting, and immunofluorescence, were employed to complement the proteomic analysis.
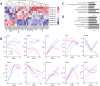
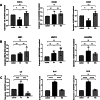
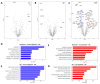
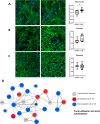
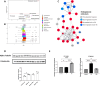
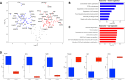
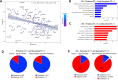
Results: Our findings revealed that oxidative stress primarily affected the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), causing notable alterations in the expression of ER-associated proteins, redox-responsive enzymes, chaperones, and sialyltransferases. These changes increased intracellular accumulation of ECM proteins and decreased secretion into the extracellular environment, indicating impaired protein trafficking and secretion. Additionally, immune-related pathways were activated in the long term, with a short-term upregulation of inflammatory markers, such as interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-18, although the levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) remained stable, indicating that not only complex inflammatory stimuli, but also oxidative stress responses can disrupt ECM homeostasis.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates a detailed proteomic view of the stress response of H2O2-treated chondrocytes, highlighting the significant changes in ER function, cytoskeletal remodeling, protein secretion, and immune responses. These changes suggest that oxidative stress impacts ECM balance and can contribute to cartilage disorders, such as OA, through different mechanisms than what is usually observed with inflammatory stimulus, offering new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying oxidative stress in chondrocytes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Prediction, screening and characterization of novel bioactive tetrapeptide matrikines for skin rejuvenation.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):92-106. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae061. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38375775
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
-
Survivor, family and professional experiences of psychosocial interventions for sexual abuse and violence: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 4;10(10):CD013648. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013648.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36194890 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 88887.612671/2021-00/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- 2022/01892-1/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2022/16532-0/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2021/14179-9/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2018/15549-1/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

