Estrogen receptor alpha dynamics and plasticity during endocrine resistance
- PMID: 40514718
- PMCID: PMC12164206
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-025-00653-8
Estrogen receptor alpha dynamics and plasticity during endocrine resistance
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is subdivided into four distinct subtypes based on the status of hormone receptors (HR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) as HER2-/HR+, HER2+/HR+, HER2+/HR- and HER2-/HR-. Among this, ERα positive breast cancer, even though they respond to endocrine treatment, half of the patients acquire resistance and progress with metastasis despite ERα status. Spatio-temporal changes in ERα and their loss under treatment pressure have been reported in a subset of patients, which is a serious problem.
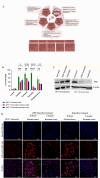
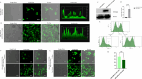
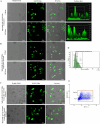
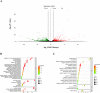
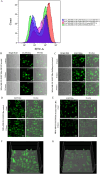
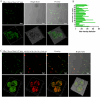
Results: We have demonstrated that in vitro-generated resistance is correlated with the down regulation of ERα. To study the ERα status transition in live cells, triple-negative breast cancer cells were engineered to express EGFP-ERα, which further supported the existence of complex intracellular signaling that regulates ERα plasticity even in unperturbed conditions. Single-cell clones generate heterogeneity and loss of expression depending on proliferative cues. However, the initial response of cells to 4 μM of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and 1 μM of endoxifen involves up-regulation of ERα, likely due to its early effect on the proteasome or autophagy pathway. Supporting this, inhibition of autophagy and the proteasome further enhanced the expression of ERα. Systematic analysis of RNA sequencing of ERα stable cells further confirmed that ERα regulates diverse intracellular signaling networks such as ubiquitin, proteasome pathways, cell proliferation and Unfolded Protein Responses (UPR), implicating its direct role in post-translational protein modifications. Cell cycle indicator probe expressing receptor-positive breast cancer cells confirmed the ERα expression heterogeneity both in 2D and 3D culture in a cell cycle phase-independent manner.
Conclusions: Overall, the study confirms the cell's intrinsic post-transcriptional mechanisms of ERα plasticity that could play a role in receptor heterogeneity and tumor progression under endocrine treatment, which warrants further investigation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Endocrine resistance; Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα); Real-time imaging; Receptor heterogeneity; TNBC; Tamoxifen; Unfolded protein response.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

