Astragaloside IV regulates FOXM1 deubiquitination to ameliorate trophoblast damage caused by high glucose
- PMID: 40514721
- PMCID: PMC12166594
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-025-00465-w
Astragaloside IV regulates FOXM1 deubiquitination to ameliorate trophoblast damage caused by high glucose
Abstract
Background: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a common metabolic complication during pregnancy that poses significant risks to both the pregnant woman and her fetus. Astragaloside IV (Ast IV) belongs to the class of triterpenoid saponins and exhibits important physiological roles in various aspects, including antidiabetic, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. The main objective of this study is to investigate the effects of Ast IV on trophoblast damage caused by high glucose (HG) and its underlying mechanism of action.
Methods: Cell viability was determined by the CCK8 assay. The levels of oxidative stress in cells were determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), malondialdehyde (MDA), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) kits. Ferroptosis in cells was assessed by the iron content kit. Gene expression levels were detected by real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot. The protein stability of Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) was determined by the cycloheximide (CHX) assay. The ubiquitination level of FOXM1 was detected by the immunoprecipitation assay.
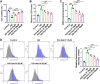
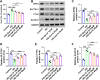
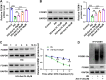
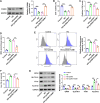
Results: Ast IV alleviated the inhibitory effect of HG on the proliferation of HTR-8/SVneo cells and reduced HG-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Ast IV was able to decrease the ubiquitination of FOXM1, thereby ensuring the stability of its expression. The overexpression of FOXM1 significantly mitigated the inhibitory effect of HG on the viability of HTR-8/SVneo cells and concurrently decreased the occurrence of HG-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis processes. Conversely, knockdown of FOXM1 diminished the protective effect of Ast IV on HTR-8/SVneo cells.
Conclusions: Ast IV ameliorates HG-induced trophoblast injury by modulating deubiquitination of FOXM1, which provides a new insight into the treatment of GDM.
Keywords: Astragaloside IV; Deubiquitination; Forkhead box protein M1; Gestational diabetes mellitus; Hyperglycemic induction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest: The authors report no conflict of interest in this work. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nesfatin-1 alleviates high glucose/high lipid-induced injury of trophoblast cells during gestational diabetes mellitus.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12789-12799. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001205. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34895049 Free PMC article.
-
Interference of KLF9 relieved the development of gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating DDAH2.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):395-406. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005929. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299612. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299612. PMID: 34787071 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-134-5p promotes inflammation and apoptosis of trophoblast cells via regulating FOXP2 transcription in gestational diabetes mellitus.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):319-330. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001219. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299586. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299586. PMID: 34969354 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Metformin ameliorates gestational diabetes mellitus via inhibiting ferroptosis of trophoblasts through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Free Radic Res. 2025 Feb;59(2):190-203. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2025.2468737. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Free Radic Res. 2025. PMID: 39959960
-
Astragaloside IV regulates the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to inhibit PM2.5-mediated lung injury in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109186. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109186. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36115280 Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Miller HC. The effect of diabetic and prediabetic pregnancies on the fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1946;29:455–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

