Ginsenoside Rg5 alleviates hypoxia-induced myocardial apoptosis by targeting STAT3 to promote Tyr705 phosphorylation
- PMID: 40514732
- PMCID: PMC12166643
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01128-8
Ginsenoside Rg5 alleviates hypoxia-induced myocardial apoptosis by targeting STAT3 to promote Tyr705 phosphorylation
Abstract
Background: The heart, as the body's blood-pumping organ, is extremely sensitive to changes in oxygen levels. Myocardial injury caused by hypoxia is a challenging issue, and there are currently no definitive specific drugs available for its treatment. Ginsenoside Rg5, one of the main rare saponins in ginseng, has shown significant efficacy in treating myocardial injury. This study aims to investigate the role and mechanisms of Rg5 in the treatment of hypoxic myocardial injury.
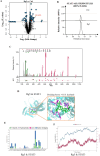
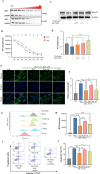
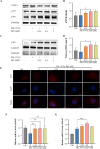
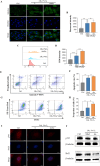
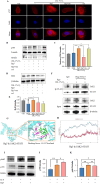
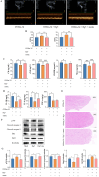
Methods: The cardioprotective effect against acute hypoxia of Rg5 was studied by assessing heart function, myocardial injury markers, inflammation, and oxidative stress in C57 mice, as well as apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Thermal proteome and target validation techniques were used to confirm the target protein of Rg5. The further protective mechanisms against hypoxia-induced damage were explored using immunocoprecipitation, immunofluorescence and rescue experiments in vivo and in vitro.
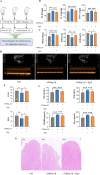
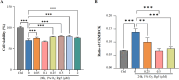
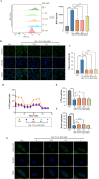
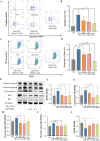
Results: The experimental results demonstrated that Rg5 effectively improved cardiac function in mice, reduced inflammation, oxidative stress, and the release of myocardial injury markers, decreased cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and lowered ROS levels. Further, using target protein screening and validation techniques, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) was verified as a direct target for Rg5's cardioprotective effect. It was observed that Rg5 specifically promoted the phosphorylation of Tyr705 in STAT3 via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, leading to the translocation of phosphorylated STAT3 into the nucleus where they induce the expression of anti-apoptotic protein and protect cells from hypoxic damage.
Conclusion: Rg5 could be a potential therapeutic agent for preventing and treating myocardial hypoxic injury, providing scientific evidence for its application in anti-hypoxic therapy.
Keywords: Ginsenoside Rg5; Hypoxia; Myocardial apoptosis; Stat3; Tyr705 phosphorylation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal care and experimental procedures in this study were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences (No: IACUC-DWZX-2023-P685). All procedures strictly followed the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Consent for publication: All authors consent to publish this manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Pan Z, Hu Y, Huang Z, Han N, Li Y, Zhuang X, Yin J, Peng H, Gao Q, Zhang W, Huang Y, Cui Y, Bi Y, Xu ZZ, Yang R. Alterations in gut microbiota and metabolites associated with altitude-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats during hypobaric hypoxia challenge. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(10):2093–113. 10.1007/s11427-021-2056-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Doutreleau S, Ulliel-Roche M, Hancco I, Bailly S, Oberholzer L, Robach P, Brugniaux JV, Pichon A, Stauffer E, Perger E, Parati G, Verges S. Cardiac remodelling in the highest city in the world: effects of altitude and chronic mountain sickness. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2022;29(17):2154–62. 10.1093/eurjpc/zwac166. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan L, Song XW, Song JC, Shi CY, Wang ZK, Huang SQ, Guo ZF, Li SH, Zhao XX, Ge JB. Downregulation of NUP93 aggravates hypoxia-induced death of cardiomyocytes in vitro through abnormal regulation of gene transcription. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(5):969–83. 10.1038/s41401-022-01036-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

