MiR-106b-5p improving the progression of chronic kidney disease by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad pathway
- PMID: 40514734
- PMCID: PMC12164090
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-025-00468-7
MiR-106b-5p improving the progression of chronic kidney disease by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad pathway
Abstract
Background: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive disorder marked by renal impairment and declining kidney function.
Aims: To investigate the expression of miR-106b-5p in CKD and its regulatory relationship with the TGF-β/Smad pathway.
Methods: A total of 150 cases of CKD patients were selected as the observation group, while 100 healthy individuals served as the control group. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was utilized to induce damage to HK-2 cells. Real-time fluorescence PCR was used to detect the expression of genes. The CCK - 8 assay was utilized to evaluate cell proliferation, while flow cytometry was applied to measure the cell apoptosis rate.
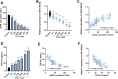
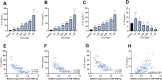
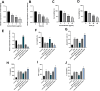
Results: miR-106b-5p is notably downregulated in CKD and exhibits a significant positive correlation with the eGFR in affected patients. Additionally, miR-106b-5p demonstrates a strong association with the levels of inflammatory factors in individuals with CKD. Furthermore, the expression of miR-106b-5p is reduced in LPS-induced HK-2 cells. Upregulation of miR-106b-5p can improve the inhibitory effect of LPS on the viability of HK-2 cells, reduce the apoptosis rate of cells, and alleviate the inflammatory response. miR-106b-5p serves as a negative regulatory factor within the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway by directly targeting the pivotal receptor TGFBR2 and the downstream effectors SMAD2/3 within the TGF-β signaling cascade.
Conclusions: miR-106b-5p ameliorates CKD progression by suppressing the TGF - β/Smad signaling pathway and could potentially be a therapeutic target for CKD.
Keywords: CKD; HK-2 cell; TGF-β/Smad; miR-106b-5p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang, University of Chinese Medicine before the study began. The written informed consent has been obtained from the participants involved. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures

References
-
- Wang B, Li ZL, Zhang YL, Wen Y, Gao YM, Liu BC. Hypoxia and chronic kidney disease. EBioMedicine. 2022; 77103942.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

