COVID-19 RT-qPCR-based screening in Austrian schools and incidences in the general population: a Bayesian spatiotemporal analysis
- PMID: 40514747
- PMCID: PMC12164201
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-025-01655-8
COVID-19 RT-qPCR-based screening in Austrian schools and incidences in the general population: a Bayesian spatiotemporal analysis
Abstract
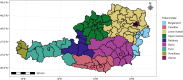
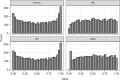
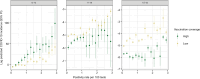
In 2021, the emergence of highly transmissible COVID-19 variants of concern increased susceptibility among younger populations. Despite this risk, face-to-face education remained essential for societal functioning and children's well-being, prompting the Austrian government to implement a nationwide screening program in educational institutions. This study explores the impact of this program on COVID-19 transmission by examining the relationship between incidence rates and factors such as age, vaccination coverage, and RT-qPCR positivity rates among school-aged children across Austrian districts, using a Bayesian spatiotemporal discrete model. Our findings highlight significant effects of vaccination and positivity rates on COVID-19 incidence, with variations in their influence across different age groups and locations. These results underscore the importance of monitoring these variables, particularly when active screening programs are in place.
Keywords: Austria; COVID-19; RT-qPCR; School; Screening; Spatiotemporal analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Written informed consent to participate in the school screening program was obtained from the participants (children and/or their guardians). The Federal Ministry of Education, Science, and Research collected anonymized data as part of the program. For this study, only aggregated, anonymized RT-qPCR data were utilized, ensuring that no individual-level information was accessible. Consequently, ethical approval was not required for the analysis of these pre-existing anonymized data. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report - 5, 25 January 2020. 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 15 Dec 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. 2024. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 6 May 2025.
-
- Pollak M, Kowarz N, Partheymüller J. Chronology of the Corona crisis in Austria - Part 4: Lockdowns, mass testing and the launch of the vaccination campaign. 2021. https://viecer.univie.ac.at/en/projects-and-cooperations/austrian-corona.... Accessed 18 Dec 2023.
-
- Österreichische Agentur für Gesundheit und Ernährungssicherheit GmbH. Coronavirus. 2023. https://www.ages.at/mensch/krankheit/krankheitserreger-von-a-bis-z/coron.... Accessed 18 Dec 2023.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

