PKN2 Inhibits VEGFA and bFGF-Mediated Angiogenesis by Targeting HIF-1α in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 40515512
- PMCID: PMC12412600
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.70050
PKN2 Inhibits VEGFA and bFGF-Mediated Angiogenesis by Targeting HIF-1α in Colon Cancer
Abstract
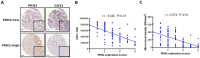
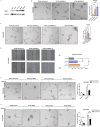
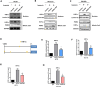
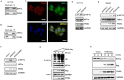
Angiogenesis plays a vital role in colon cancer growth and metastasis. The role of protein kinase N2 (PKN2) in colon cancer is rarely studied. In this study, we investigated the effect of PKN2 on angiogenesis in colon cancer. We evaluated the correlation between PKN2 expression and microvessel density (MVD) in tumor tissue of patients with colon cancer. The effect of PKN2 on tumor angiogenesis was investigated both in cultured colon cancer cells and in a mouse colon cancer model. PKN2 targeted vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) expression, and secretion were analyzed, and the specific regulatory role of PKN2 on HIF was explored. PKN2 expression was negatively correlated with tumor MVD in tumor tissue of patients with colon cancer. PKN2 inhibited angiogenesis in both in vitro and in vivo models of mouse tumors. Mechanistically, PKN2 suppressed the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and reduced its nuclear accumulation, leading to the inhibiting of VEGFA and bFGF transcription by preventing HIF-1α binding to their promoters. Additionally, PKN2 directly interacted with HIF-1α at the protein level and induced phosphorylation, resulting in ubiquitination-dependent degradation of HIF-1α in colon cancer cells. Our study demonstrated, for the first time, that PKN2 exerts inhibitory effects on tumor angiogenesis in colon cancer. We propose a novel mechanism by which PKN2 regulates VEGFA and bFGF expression through modulation of the dynamic equilibrium of HIF-1α protein levels.
Keywords: HIF‐1α; PKN2; colon cancer; tumor angiogenesis.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82473012/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81802339/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024A1515030242/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2022A1515012406/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- SL2022A03J01176/Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

