Optimizing management of stage IV EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer in Asia: An expert opinion
- PMID: 40515576
- PMCID: PMC12375841
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.35512
Optimizing management of stage IV EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer in Asia: An expert opinion
Abstract
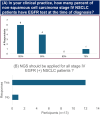
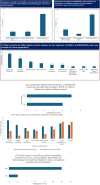
Lung cancer is Asia's most prevalent cancer, accounting for the highest global patient share. A significant number of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients in Asia exhibit mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Although clinical outcomes are improving with newer therapies, challenges persist in the effective management of EGFR mutant (EGFRm) NSCLC. Given the substantial disease burden, understanding the current diagnostic and treatment patterns for EGFRm NSCLC from an Asian perspective is essential. This expert opinion presents recommendations from Asian experts on molecular testing and treatment of first-line and second-line EGFRm NSCLC. The recommendations aim to optimize patient outcomes by providing a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management, considering the high prevalence of EGFR mutations in the Asian population. The experts discussed and recommended approaches for optimal management of EGFRm NSCLC. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing is recommended to be included in the reimbursement scheme, and the turnaround time of testing should be shortened, considering the high burden of the disease in Asia. The panel recommended careful selection of patients for osimertinib+chemotherapy or lazertinib+amivantamab based on safety and efficacy profile, patient age, and disease status. While the panel agreed that osimertinib+chemotherapy is acceptable for these patients, dose adjustment and careful patient selection are recommended to optimize safety outcomes. For lazertinib+amivantamab, measures to mitigate adverse events such as the use of pre-medication with steroids, prophylactic anticoagulants, and dose modification are recommended. For patients progressing on one of the combination regimens, experts recommended repeat NGS testing and continued treatment with chemotherapy.
Keywords: Asian exert opinion; EGFR positive NSCLC; EGFRm NSCLC; NSCLC in Asia.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Gee‐Chen Chang has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Hoffman‐La Roche, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb. Akhil Kapoor has served as an investigator on multiple clinical trials for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Erixis, MSD, and Novartis. All grants in this regard were paid to the institution. Chee Khoon Lee has received honoraria and grants from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Janssen, GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Roche, Gilead, Novartis, and Glenmark, and meeting/travel support from AstraZeneca and Janssen. Chunxia Su declares no conflict of interest for this study. Daniel Chan and Moushumi Suryavanshi have received consulting fees from AstraZeneca. Guia Elena Imelda Ladrera has served on the advisory board and received honoraria and travel expenses from AstraZeneca. Hye Ryun Kim received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, stock ownership in Bridgebio Therapeutics; served in a consultation or advisory role for Bayer, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Yuhan; and received research funding from the Yonsei Lee Youn Jae Fellowship outside of the current study. Mostafa Aziz Sumon reports no conflict of interest. Sita Andarini has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Darya Varia, Etana, GOF, Hetero, JNJ, Kalgen Innolab, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, ZuelligPharma Therapeutics, travel grants from AstraZeneca, Darya Varia, Etana, GOF, Hetero, JNJ, Kalgen Innolab, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, ZuelligPharma Therapeutics, and has served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Darya Varia, JNJ, MSD. Tatsuya Yoshida has received grants from Novartis, AbbVie, Amgen, Daiichi‐Sankyo, AstraZeneca, MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Merck Biopharma, honoraria from Novartis, Daiichi‐Sankyo, AstraZeneca, MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, BMS, Ono, Takeda, Pfizer, Lilly, and Merck Biopharma, and has been a member of the advisory board for Novartis, MSD, Amgen, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Thanyanan Reungwetwattana received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, J&J, Pfizer, Amgen, Takeda, MSD; served on advisory board for AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, J&J, Pfizer, Amgen, Takeda, Yuhan, MSD; and a grant for clinical research was paid to the institution by AstraZeneca, Roche, MSD, Yuhan. Tuan Khoi Nguyen has received grants from MSD, Roche, and AstraZeneca; honoraria, travel support, and consulting fees from MSD, Roche, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Pfizer, and Pierre Fabre. Pei Jye Voon has received grants/contracts from Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen‐Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Viracta Therapeutics Inc., ROCHE, Merck KGaA, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Beigene, Amgen, Revolutionary Medicine; consulting fees from Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Beigene, Amgen, Merck KGaA, Janssen‐Cilag, Johnson & Johnson; and honoraria payments from Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Amgen, Merck KGaA, Janssen‐Cilag, Johnson & Johnson.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer Today [Internet]. https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/
-
- Zheng M. Classification and pathology of lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25(3):447‐468. - PubMed
-
- Lam WK. Lung cancer in Asian women‐the environment and genes. Respirology. 2005;10(4):408‐417. - PubMed
-
- Lam DC, Liam CK, Andarini S, et al. Lung cancer screening in Asia: an expert consensus report. J Thorac Oncol. 2023;18:1303‐1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

