USP10 promotes the progression and attenuates gemcitabine chemotherapy sensitivity via stabilizing PLK1 in PDAC
- PMID: 40517136
- PMCID: PMC12167373
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07757-z
USP10 promotes the progression and attenuates gemcitabine chemotherapy sensitivity via stabilizing PLK1 in PDAC
Abstract
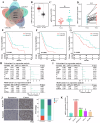
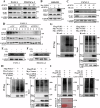
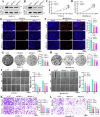
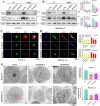
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most malignant tumors with limited treatment options, and chemotherapy resistance contributes to poor prognosis. An increasing number of studies have shown that ubiquitin specific peptidases (USPs), a subtype of deubiquitinases, can affect tumor progression by regulating the stability or biological function of substrate proteins. Thus, USPs are becoming attractive targets for cancer treatment. In this study, we investigated the role of USPs in PDAC. This study illustrated significant upregulation of USP10 expression in PDAC, which was found to be correlated with unfavorable prognosis. Further evaluation showed that USP10 exhibited the ability to facilitate PDAC progression in vitro and in vivo. The assays of immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry, CO-IP, and GST pull-down suggested that USP10 directly interacted with PLK1. Deubiquitination assays indicated that USP10 could reduce the ubiquitination of PLK1 and increase protein stability. Moreover, USP10 may promote autophagy in PDAC cells through PLK1 and further attenuate the response of PDAC cells to gemcitabine (GEM). Finally, we demonstrated that the inhibition of USP10 combined with GEM synergistically inhibited the progression of PDAC in vitro and in vivo. In summary, we revealed that USP10, as a tumor promoter, promoted the progression and attenuated GEM chemotherapy sensitivity via stabilizing PLK1 in PDAC, providing a potential target for the treatment of PDAC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Li O, Li L, Sheng Y, Ke K, Wu J, Mou Y, et al. Biological characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: initiation to malignancy, intracellular to extracellular. Cancer Lett. 2023;574:216391. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63. - PubMed
-
- Mizrahi JD, Surana R, Valle JW, Shroff RT. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2020;395:2008–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

