Perivascular space fluid diffusivity predicts clinical deterioration in prodromal and early-stage Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40517151
- PMCID: PMC12167374
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-01036-6
Perivascular space fluid diffusivity predicts clinical deterioration in prodromal and early-stage Parkinson's disease
Abstract
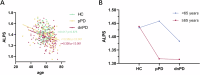
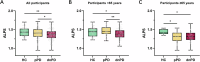
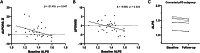
The glymphatic system is essential for clearing toxic proteins from the brain, and understanding its dysfunction in the early stages of Parkinson's disease (PD) may facilitate the development of disease-modifying therapies. This study aimed to evaluate alterations in glymphatic function and its correlation with disease progression in prodromal and early clinical stages of PD. Participants were categorized into three groups: prodromal PD (pPD), de novo PD (dnPD), and healthy controls (HCs), further divided by age. Glymphatic function was assessed using the ALPS index derived from diffusion tensor imaging. Results indicated that the ALPS index was significantly lower in older pPD and dnPD patients, correlating with various clinical symptoms. Longitudinal analysis revealed a decrease in the ALPS index over time in pPD patients who progressed to clinical PD, while it remained stable in non-converters. Additionally, the baseline ALPS index was predictive of the progression of both motor and non-motor symptoms in pPD patients. In dnPD patients, a lower baseline ALPS index predicted the progression of motor symptoms in the older subgroup. Overall, the ALPS index is reduced in the early stages of PD and may serve as a predictor for disease progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mehra, S., Sahay, S. & Maji, S. K. α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: implications in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom.1867, 890–908 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Foltynie, T. et al. Medical, surgical, and physical treatments for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet403, 305–324 (2024). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82371268/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20231125/Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- 2020ZX17/Science and Technology Development Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangsu Province
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- K2023031/Medical research key project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission
- LZ24H180002/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LZ24H180002/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

